Elevations
Contents |
[edit] What is orthographic projection?
Orthographic projection is a technique for drawing a three dimensional object in two dimensions, by ‘projecting’ its surfaces into a two dimensional representation, where the projection lines are orthogonal to (perpendicular to) the projection plane (that is, there is no foreshortening or perspective).
[edit] What are elevation drawings?
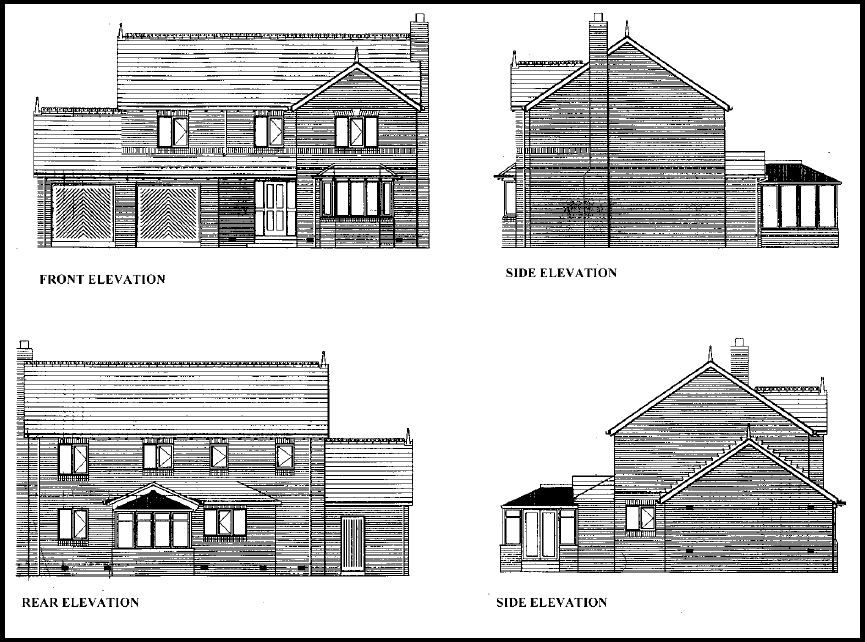
In the construction industry, the term ‘elevation’ refers to an orthographic projection of the exterior (or sometimes the interior) faces of a building, that is, a two-dimensional drawing of the building’s façades. An elevation drawing is a first angle projection that shows all parts of the building as seen from a particular direction with the perspective flattened. Generally, elevations are produced for four directional views, for example, north, south, east, west.
[edit] What should elevation drawings include?
Simple elevation drawings might show:
- The outline of a building.
- The exterior walls, and sometimes the finishes of the walls.
- Openings such as doors and windows.
- Roofing.
- Exterior features such as chimneys, decks, porches and steps.
- Any portion of the foundation that may be visible.
- Projections such as eves and rainwater pipes.
- Level datums such as finished ground level and floor positions.
- Key dimensions such as wall lengths and heights.
- A title block, including the name, number and revision of the drawing, the date of preparation, who the drawing was prepared by, project details, drawing scale, north point and so on.
However, they can contain a great deal more detail depending on the complexity of the buildings the reason for their preparation.
Insufficient information on elevations can mean that they do not properly satisfy the need for which they were prepared, however, very detailed elevations can be time-consuming and expensive to prepare and confusing to read. It is important therefore that the reason for the drawing is clear and the level of detail required satisfies that need.
[edit] What are elevations used for?
Elevations might be prepared for a number of reasons, including:
- As part of a survey of existing buildings.
- To create a record of an existing building.
- To explore and communicate interior and exterior design options.
- As part of an application for planning permission.
- As part of an application for building regulations approval.
- To communicate construction information.
- For sales and marketing.
[edit] How are elevations prepared?
Historically, buildings have been drawn by hand on two dimensional paper, and so orthogonal projection and the drawing of two dimensional plans and elevations have been the standard means of representation.
However, increasingly, buildings are being drawn using computer aided design (CAD) or building information modelling (BIM) software that represents them in three dimensions. Where these digital methods of drawing create 3d model of the building, two-dimensional elevations can be generated automatically from the 3D models, they do not need to be drawn individually.
[edit] Alternative meaning of elevation
The term 'elevation' might also be used to refer to the height of something above or below a fixed reference point or datum.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- As-built drawings and record drawings
- Assembly drawing.
- Building information modelling.
- CAD layer.
- Computer aided design.
- Concept drawing.
- Detail drawing.
- Engineering drawing.
- Façade.
- Floor plan.
- General arrangement drawing.
- Notation and symbols.
- Orthogonal plan.
- Paper sizes.
- Principal elevation.
- Projections.
- Scale drawing.
- Standard hatching styles for drawings.
- Superelevation.
- Technical drawing.
- Techniques for drawing buildings.
- Types of drawings for building design.
- Working drawing.
[edit] External references
- The House Plans Guide – Elevation drawings
Featured articles and news
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.
Cutting carbon, cost and risk in estate management
Lessons from Cardiff Met’s “Halve the Half” initiative.
Inspiring the next generation to fulfil an electrified future
Technical Manager at ECA on the importance of engagement between industry and education.
Repairing historic stone and slate roofs
The need for a code of practice and technical advice note.
Environmental compliance; a checklist for 2026
Legislative changes, policy shifts, phased rollouts, and compliance updates to be aware of.
UKCW London to tackle sector’s most pressing issues
AI and skills development, ecology and the environment, policy and planning and more.
Managing building safety risks
Across an existing residential portfolio; a client's perspective.
ECA support for Gate Safe’s Safe School Gates Campaign.
Core construction skills explained
Preparing for a career in construction.
Retrofitting for resilience with the Leicester Resilience Hub
Community-serving facilities, enhanced as support and essential services for climate-related disruptions.
Some of the articles relating to water, here to browse. Any missing?
Recognisable Gothic characters, designed to dramatically spout water away from buildings.
A case study and a warning to would-be developers
Creating four dwellings... after half a century of doing this job, why, oh why, is it so difficult?
Reform of the fire engineering profession
Fire Engineers Advisory Panel: Authoritative Statement, reactions and next steps.
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.






















Comments
[edit] To make a comment about this article, or to suggest changes, click 'Add a comment' above. Separate your comments from any existing comments by inserting a horizontal line.