Housing related Acts index
- 2022 Healthy Homes Bill. UK Government.
- 2022 Building Safety Act. UK Government: A Bill to make provision about the safety of people in or about buildings and the standard of buildings, to amend the Architects Act 1997, and to amend provision about complaints made to a housing ombudsman.
- 2016 Housing and Planning Bill. UK Government: An Act of Parliament that makes changes to housing policy and the planning system. It introduces legislation to allow the sale of higher value local authority homes, introduce starter homes and "Pay to Stay" and other measures intended to promote home ownership and boost levels of housebuilding.
- 2012 Welfare Reform Act. UK Government: This act introduced the Bedroom tax or under-occupancy penalty, which reduced the amount of benefit paid to claimants if they are deemed to have too much living space in the property they are renting
- 2004 Planning and Compulsory Purchase Act. UK Government: Aimed to make the planning application process quicker and more efficient and increasing the predictability of planning decisions. Speeding up of the handling of major infrastructure projects. Reforming and speeding up of the plans system. Replacing local plans, unitary development plans and structure plans with local development documents.
- 1996 Party Wall etc Act. UK Government: Regulations for building, altering or settling disputes regarding party walls.
- 1996 Housing Grants, Construction and Regeneration Act. UK Government: Amendments to improvement and repair grant systems. Abolition of mandatory grants.
- 1996 Housing Act. UK Government: Amendments to housing benefit, tenants' rights and homelessness. New regulatory framework for 'Registered Social Landlords'
- 1995 Disability Discrimination Act. UK Government: Introduced proposals to make limited wheelchair access mandatory for all new build housing.
- 1993 Housing and Urban Development Act. UK Government: Compulsory Competitive Tendering (CCT) in London housing. Rent to mortgage scheme.
- 1990 Town and Country Planning Act. UK Government: Sets out the statutory definition of 'development' for planning permission.
- 1989 Local Government and Housing Act. UK Government: Local councils lost their right to subsidize council rents out of local revenue. New local authority rent and subsidy systems.
- 1988 Housing Act. UK Government: The act removed rent control in the private sector, thus promoting the private sector in the provision of 'affordable' housing and move to mix funding for housing associations. Central government could designate an area of public housing and create a Housing Action Trust (HAT) to manage the houses. The act redefined housing associations as non-public bodies, permitting access to private finance, which was a strong motivation for transfer as public sector borrowing had been severely constrained.
- 1986 Housing and Planning Act. UK Government: Facilitated block sales of estates and increased 'Right to Buy' discounts.
- 1986 Building Societies Act. UK Government: Enabled building societies to own and invest in housing directly and to compete with other financial institutions.
- 1985 Housing Act. UK Government: The act (as well as the 1988 act) facilitated the transfer of council housing to not-for-profit housing associations. Right to repairs. Section 325 of the Housing Act 1985 provides that there is overcrowding wherever there are so many people in a house that any two or more of those persons, being ten or more years old, and of opposite sexes, not being persons living together as husband and wife, have to sleep in the same room.
- 1984 Housing Defects Act. UK Government: Obligations placed on local authorities in respect of sold defective dwellings.
- 1984 Building Act. UK Government: This act obliges local authorities to enforce the building regulations in their areas.
- 1982 Social Security and Housing Benefits Act. UK Government: Established housing benefit system
- 1980 Housing Act ('Right to Buy'). UK Government: Under this act, the government gave council tenants with a three year history of tenancy a right to buy their homes at generous discounts. These ranged from a third to a half the value of the property. Between 1979 and 1987, more than a sixth of the total stock of council houses were sold.
- 1980 Planning and Land Act. UK Government: It is responsible for the establishment of development corporations, including the London Docklands Development Corporation. It also created the Public Request to Order Disposal, which can be used by the government to force a local authority to sell derelict land and empty property owned by certain public landlords.
- 1975 Housing Rents and Subsidies Act. UK Government: The act reversed the policy of 'fair' rents and empowered local authorities to set rent levels.
- 1974 Health & Safety etc. UK Government: Introduction of national building regulations to replace local byelaws.
- 1974 Local Government Act. UK Government: Grants for Housing Associations enabling large-scale development.
- 1974 Housing Act. UK Government: Extended functions of Housing Corporation, provided for the registration and giving of assistance to housing associations, introduced new powers for declaration of Housing Action Areas and made provisions for higher renovations grants.
- 1972 Housing Finance Act. UK Government. Reduced council housing subsidy and replaced controlled rents with 'fair' rents - in effect a rent increase
- 1972 Local Government Act. UK Government.
- 1972 The Building Regulations. UK Government.
- 1969 Housing Act. UK Government: Funds would be channelled towards the improvement of existing housing. It recommended a new policy, the General Improvement Areas (GIAs), for which subsidies would be available
- 1968 Town and Country Planning Act. UK Government: Protection of listed buildings.
- 1967 Leasehold Reform Act. UK Government. The Act grants the right to long leaseholders of houses let at low and moderately low rents to buy their homes compulsorily from their landlords at a fair price.
- 1967 Housing Subsidies Act. UK Government: Provided for financial assistance towards the provision, acquisition, or improvement of dwellings.
- 1965 Rent Act. UK Government: The act invoked the criminal law to deal with abuses by landlords and established a system of 'fair rents'.
- 1965 New Towns Act. UK Government: The act authorised the government to designate areas as new towns, and passing development control functions to a New Town Development Corporation.
- 1964 Protection from Eviction Act. UK Government: Imposed sanctions of landlords who evicted without a court order.
- 1964 Housing Act. UK Government: Birth of the Housing Corporation
- 1962 Landlord and Tenant Act. UK Government
- 1961 Housing Act. UK Government: Gave local authorities powers to limit the number of people living in a property in an attempt to prevent overcrowding.
- 1961 Public Health Act. UK Government: The Public Health Act of 1961 was the statutory instrument and the first regulations were published in 1965.
- 1959 House Purchase and Housing Act. UK Government: The government's policy of encouraging owner occupation ran into problems, limited by high interest rates. Building societies agreed to pay an increased rate of interest on government loans used to fund mortgages.
- 1958 Landlord and Tenant (Temporary Provisions) Act. UK Government: The act brought some relief from the 1957 Rent Act.
- 1957 Rent Act. UK Government: It allowed a substantial increased on controlled rent.
- 1957 Housing Act. UK Government: Encouraged increases in rent and enabled local authorities to sell stock, encouraging privatisation. Effect of this act was increasing rents, by 60% between 57 and 59 (partially leading to Labour party winning the 64 election)
- 1956 Housing Subsidies Act. UK Government: Funds were only made available for slum clearance and housing provision for slum dwellers. Encouraged high-rise.
- 1954 Housing Rent and Repairs Act. UK Government: Sought to encourage landlords to repair controlled houses by allowing a "repairs increase" in the rent for houses brought into.
- 1952 Housing Act. UK Government: Raised subsidy to local authorities, encouraging publicly funded building. Under the 1952 Housing Act local authorities were allowed to sell council houses, and the value of buildings without a licence increased.
- 1952 Town Development Act. UK Government: The act to encouraged town development in county districts for the relief of congestion
- 1949 Housing Act. UK Government: Enabled local authorities to acquire homes for improvement or conversion with 75% Exchequer grants. It also removed the restriction imposed upon local authorities by previous pieces of housing legislation which limited them to providing housing for working-class people only.
- 1947 Town and Country Planning Act. UK Parliament: The Act established that planning permission was required for land development, ownership alone no longer conferred the right to develop the land.
- 1946 (Housing (Financial and Miscellaneous Provisions) Act) UK Parliament : Provided large subsidies for the construction of council housing.
- 1946 New Towns Act (UK Parliament): The 1946 New Towns Act established an ambitious programme for building new towns. It gave the government power to designate areas of land for new town development. Many were intended to accommodate the overpopulation from London & Greater London Authoritysgow. But others were built to provide better quality housing for existing employment areas and other were located in mining areas.
- 1944 Housing (Temporary Accommodation) Act (UK Parliament/ Ministry of Reconstruction): The Government aimed to provide enough homes for each family who required an individual dwelling, which it perceived had been the situation in 1939 prior to the outbreak of war. It also intended for the completion of the pre-war slum clearance project. It provided an increase in the labour force of the building industry and the construction of at least 300,000 homes during the two-year period after the act (Emergency Factory Made programme). It aimed to prevent price inflation caused by high demand on building services, subsidise privately built houses, and to provide for the construction of temporary, prefabricated housing.
- 1936 (Public Health Act( (UK Parliament): Required all local authorities to adopt building byelaws.
- 1935 Housing Act (UK Parliament) It required every local authority to submit a programme of building and demolition aimed at eliminating slums from their area.
- 1933 Housing Act (Financial Provisions) (UK Parliament) It ended subsidies for general housing, that were present in the Greenwood Act, authorities were required to concentrate their efforts on slum clearance.
- 1930 Housing Act (Greenwood's Act) (UK Parliament) Encouraged mass slum clearance and councils set to work to demolish poor quality housing and replace it with new build. Populations of more than 20,000 needed to prepare 5 yr plan to deal with slums. Houses created were smaller and narrow fronted, no trees, expenditures had dropped 40%
- 1929 Housing (Revision of Contributions) Act (UK Parliament)
- 1925 Law of Property Act (UK Parliament) Passed with Land Registration Act, the Trustee Act 1925, the Settled Land Act 1925 and the Land Charges Act 1925
- 1924 Housing (Financial Provisions) Act (Wheatley Act) (UK Parliament) The Act allowed central government to provide subsidies to build public housing.
- 1923 Housing Act (UK Parliament) Reduced the housing subsidy to local authorities
- 1919 Housing, Town Planning, &c. Act 1919 (Addison Act) (UK Parliament): The Act was passed to allow the building of new houses after World War I. Provided subsidies to local authorities to help finance the construction of 500,000 houses within three years (only 213,800 homes were built). This legislation subsidised the cost of council housing from three sources: rents, local authority rates, and a grant from the state (previously there had not been no subsidies).
- 1885 Housing of the Working Classes Act (UK Parliament) Consolidated and amended Shaftesbury, Torrens, and Cross Acts. Lodging houses were redefined to include separate dwellings for labouring classes. The interests for Public Works Loan Board lowered.
- 1884 London Building Act (London County Council (LCC)/ Banister Fletcher)
- 1882 Artisans’ Dwellings Act (UK Parliament) Combined Torrens' and Cross' Act and aimed to improve the procedures for purchase, demolition and re-housing.
- 1875 Artizans’ and Labourers’ Dwellings Improvement Act (Cross' Acts) (UK Parliament) Carried out by the Metropolitan Board of Works and the City Commissioners of Sewers. The act controlled the clearance of slums and aimed to build replacement dwellings for the working-classes. They requested that the local Medical Officer of Health for the vestry or district should prepare a report comparing the mortality rate within area with other parishes. Justification for clearance was usually based solely on high mortality rates.
- 1868 Torrens' Act (UK Parliament) This Act made housing owners responsible to demolish or repair insanitary dwellings and to keep their properties in a habitable state.
- 1868 Artizans and Labourers Dwelling Act
- 1858 Local Government Act (UK Parliament) Local authorities had the power to make and adopt building byelaws as a means of controlling the construction of building.
- 1851 Labouring Classes Lodging Houses Act (UK Parliament) Allowed local authorities to borrow money to set up and operate lodging houses for the labouring classes.
- 1851 Common Lodging Houses Act (Shaftesbury Act) (UK Parliament): Considered by some as the first housing legislation. It gave boroughs and vestries the power to raise funds via local rates or Public Works Loan Commissioners to build lodging houses for unmarried working people.
- 1848 Public Health Act (UK Parliament): Act was passed after much campaigning by the Health of Towns Association, and another severe outbreak of cholera in 1848. It established a Central Board of Health (limited powers and no money). Those boroughs that had already formed a Corporation were to assume responsibility for drainage, water supplies, and paving. Loans could be made for public health infrastructure which were paid back from the rates.
- 1847 Towns Improvement Clauses Act (UK Parliament): Act for paving, draining, cleansing, lighting, and improving towns.
- 1840 Building Act (Parliament of Great Britain): The Act enables the regulation requirements to be altered and improved without further parliamentary improvement.
- 1774 Building Act (Fires Prevention (Metropolis) Act) (Parliament of Great Britain): Categorised urban houses into different rates defined by the value of the property and its total floor area. It standardised the quality and construction of buildings and made the exterior of a building as fire-proof as possible, by restricting any superfluous exterior timber ornamentation except for door frames and shop fronts. Appointment of District Surveyors to supervise the Building Laws.
- 1772 The London Building Act (Parliament of Great Britain): Established party wall requirements.
- 1667 Rebuilding of the City of London(Parliament of Great Britain): The Act proposed that all new buildings had to be constructed of brick or stone for fire safety. It also imposed a maximum number of storeys per house for a fixed number of abodes to eliminate overcrowding.
[edit] External Links
Featured articles and news
Shortage of high-quality data threatening the AI boom
And other fundamental issues highlighted by the Open Data Institute.
Data centres top the list of growth opportunities
In robust, yet heterogenous world BACS market.
Increased funding for BSR announced
Within plans for next generation of new towns.
New Towns Taskforce interim policy statement
With initial reactions to the 6 month policy update.
Heritage, industry and slavery
Interpretation must tell the story accurately.
PM announces Building safety and fire move to MHCLG
Following recommendations of the Grenfell Inquiry report.
Conserving the ruins of a great Elizabethan country house.
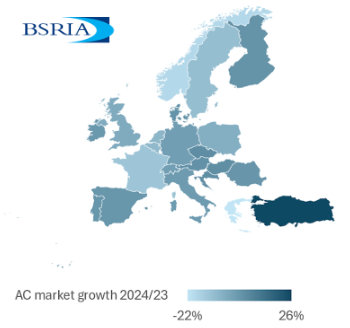
BSRIA European air conditioning market update 2024
Highs, lows and discrepancy rates in the annual demand.
50 years celebrating the ECA Apprenticeship Awards
As SMEs say the 10 years of the Apprenticeship Levy has failed them.
Nominations sought for CIOB awards
Celebrating construction excellence in Ireland and Northern Ireland.
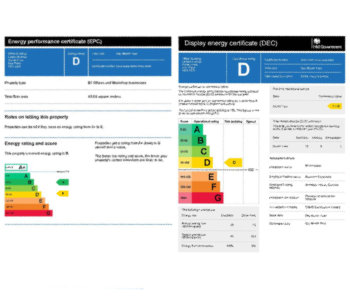
EPC consultation in context: NCM, SAP, SBEM and HEM
One week to respond to the consultation on reforms to the Energy Performance of Buildings framework.
CIAT Celebrates 60 years of Architectural Technology
Find out more #CIAT60 social media takeover.
The BPF urges Chancellor for additional BSR resources
To remove barriers and bottlenecks which delay projects.
Flexibility over requirements to boost apprentice numbers
English, maths and minimumun duration requirements reduced for a 10,000 gain.
A long term view on European heating markets
BSRIA HVAC 2032 Study.
Humidity resilience strategies for home design
Frequency of extreme humidity events is increasing.
National Apprenticeship Week 2025
Skills for life : 10-16 February