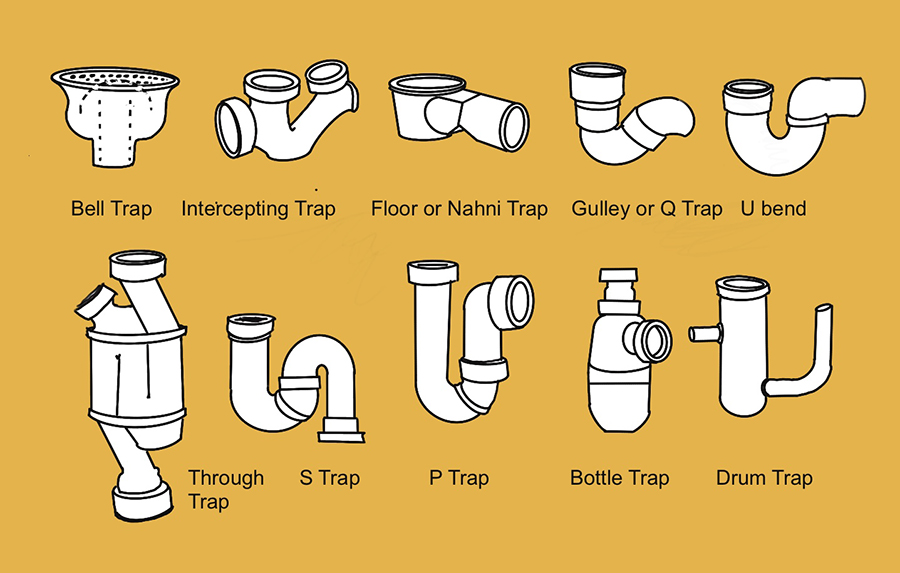
Types of waste trap
Contents |
[edit] What are waste traps?
Waste traps or traps are small plumbing devices designed to prevent odours from sewage or waste water leaving the pipe systems and entering the interior spaces of buildings. They can also help prevent the spread of bacteria and insects.
They are simple but ingenious devices that generally work by creating an air trap using the waste water of the system, which sits in a small reservoir within in the line of the waste water flow. It is normally a relatively simple plumbing part used in sinks, toilets, showers, baths as well as floor level drains, coming in a variety of types with various terms associated.
[edit] Types of waste trap
Some of the more common types of waste trap are described below.
[edit] U-bend
The U-bend is possibly the most common term used to describe a waste trap in the UK. The variations on this type all contain a U shaped form in their design. The U trap was invented by the English businessman plumber T.Crapper in the late 1800's and was an improvement on the S trap which was invented some 100 years earlier.
[edit] S trap
The S trap was invented by A.Cumming who also patented the first flush toilet, it developed into the U-bend, which was an improvement because it did not need an overflow pipe.
Shallow or low-level U-traps are based on the same system as the U-bend, but are shallow so that they fit into tight spaces such as underneath showers and bath units.
[edit] Gully or Q trap
A gully trap or Q trap has a basin in the ground with a water seal for odours and a vent pipe to allow fresh air in.
[edit] Floor or nahni trap
A floor or nahni trap is a shallow design of minimum 50 mm depth provided in the floor to drain and prevent smells entering internal spaces. Nahni is indian for washing area, where these are commonly used.
[edit] Interceptor trap
Interceptor traps normally act between the main sewer and building sewer, they have deep water seals of 100 mm to prevent bugs and insects crossing systems and are usually found in the outlet of the last manhole chamber from a property before the main sewer connection and are typically made of vitreous clay. There are many different types such as: The Winser trap, Kenon trap, Bristol trap, Buchan trap, Reverse Interceptor trap, The Radnor, The Netley (reverse action), The Warwick, The Coulsdon and The Salus.
[edit] Bell trap
A bell trap contains a water reservoir cup which has a bell shaped cover over it that dips at the edges into the water filled cup to form a seal.
[edit] Straight-through trap
A straight-through trap or through trap is a compact trap specifically allowing for neat plumbing behind basin pedestals.
[edit] P-trap
A P-trap is a u-shaped bend in a waste pipe,containing sitting water, that connects a sink's drain to a septic tank or main sewer system.
[edit] Bottle trap
A bottle trap is attached under a sink to block gases from rising from a drainage systems into a bathroom.
[edit] Drum trap
Drum traps are often found in older systems functioning in a similar way to bottle traps.
[edit] Other type or names for traps
Grease trap, running trap, low-level bath trap etc..
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
Homes England creates largest housing-led site in the North
Successful, 34 hectare land acquisition with the residential allocation now completed.
Scottish apprenticeship training proposals
General support although better accountability and transparency is sought.
The history of building regulations
A story of belated action in response to crisis.
Moisture, fire safety and emerging trends in living walls
How wet is your wall?
Current policy explained and newly published consultation by the UK and Welsh Governments.
British architecture 1919–39. Book review.
Conservation of listed prefabs in Moseley.
Energy industry calls for urgent reform.
Heritage staff wellbeing at work survey.
A five minute introduction.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Showcasing the very best electrotechnical and engineering services for half a century.
Welsh government consults on HRBs and reg changes
Seeking feedback on a new regulatory regime and a broad range of issues.
CIOB Client Guide (2nd edition) March 2025
Free download covering statutory dutyholder roles under the Building Safety Act and much more.
Minister quizzed, as responsibility transfers to MHCLG and BSR publishes new building control guidance.
UK environmental regulations reform 2025
Amid wider new approaches to ensure regulators and regulation support growth.
BSRIA Statutory Compliance Inspection Checklist
BG80/2025 now significantly updated to include requirements related to important changes in legislation.