Heat source
Heat is the energy that is transferred between different systems as a result of thermodynamic interactions. Heat differs from temperature, which is a measure of the average kinetic energy of molecules. Temperature will tend to vary throughout a body depending on its heat exchange with its surroundings
In the built environment, heat may be used to:
- Create comfortable conditions for occupants.
- To prevent condensation.
- For activities such as drying and cooking.
- For industrial processes.
A heat source is a system from which heat is ‘lost’ to a heat sink. For example, in the built environment, a radiator may be considered to be a heat source, whilst the space around it, which it heats by a process of radiation and convection, might be considered to be a heat sink.
Heat sinks might also refer more specifically to active devices that transfer heat from a system to a medium that dissipates that heat away from the system, and in so doing cooling it. Heat sink devices are commonly used to cool computers.
Anything may behave as either a heat source or a heat sink depending on its temperature compared to its surroundings, however, in the building environment a number of elements are exploited specifically for their characteristics as heat sources for functions such as helping create thermal comfort.
This might include:
- The sun.
- The ground (eg ground source heat pumps, geothermal piles).
- The air (eg air source heat pumps).
- Water (eg water source heat pumps).
- Thermal mass (such as an exposed concrete slab).
- Heating devices such as radiators, electric heaters, open fires, wood-burning stoves and so on.
Other items might act as inadvertent heat sources, which may not be desirable as they may cause overheating, such as people, computers, ovens and other equipment. These heat sources are sometimes referred to as heat loads.
Heat sinks might include air conditioning systems, refrigeration equipment, thermal mass and so on.
Heat sources and heat sinks such as thermal mass might be described as ‘passive’ in that they use the layout, fabric and form of a building to reduce or remove the need for ‘active’ systems such as heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Boiler.
- Building heating systems.
- Conduction.
- Convection.
- Ground source heat pumps.
- Heat.
- Heat interface units.
- Heat meter.
- Heat pump.
- Heat recovery.
- Heat transfer.
- National heat map.
- Overheating.
- Radiant heating.
- Radiation.
- Solar gain.
- Thermal comfort.
- Thermal mass.
- Types of domestic heating system.
Featured articles and news
A case study and a warning to would-be developers
Creating four dwellings... after half a century of doing this job, why, oh why, is it so difficult?
Reform of the fire engineering profession
Fire Engineers Advisory Panel: Authoritative Statement, reactions and next steps.
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this...
National Apprenticeship Week 2026, 9-15 Feb
Shining a light on the positive impacts for businesses, their apprentices and the wider economy alike.
Applications and benefits of acoustic flooring
From commercial to retail.
From solid to sprung and ribbed to raised.
Strengthening industry collaboration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong Institute of Construction and The Chartered Institute of Building sign Memorandum of Understanding.
A detailed description from the experts at Cornish Lime.
IHBC planning for growth with corporate plan development
Grow with the Institute by volunteering and CP25 consultation.
Connecting ambition and action for designers and specifiers.
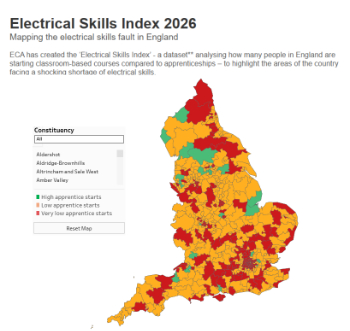
Electrical skills gap deepens as apprenticeship starts fall despite surging demand says ECA.
Built environment bodies deepen joint action on EDI
B.E.Inclusive initiative agree next phase of joint equity, diversity and inclusion (EDI) action plan.
Recognising culture as key to sustainable economic growth
Creative UK Provocation paper: Culture as Growth Infrastructure.