Cordwood
Cordwood is a term used to describe a pile of wood that is cut into lengths of a similar size and stacked in a single row. The term can describe wood that has been stacked as a storage method for firewood, but it can also be used to describe a stack of wood used to construct a wall, often with lime mortar in between and sometimes referred to as a stackwall.
In the US, more specifically, a full cord of wood is a stack of timber firewood lengths that is 4 feet tall, 8 feet long, and 4 feet deep (1.2 by 2.4 by 1.2 metres deep). Face chord describes the same surface area of a wood stack but where the depth of the wood is only 16 inches, about a third of a full chord or less than half a metre in depth.
Cordwood construction is a construction method that uses end-grain logs of varying lengths stacked to form walls, usually with mortar in between. In his book Essential Cordwood Building: The complete step-by-step guide (New Society Publishers, 2018; Gabriola Island, Canada), Rob Roy suggests a common mix by volume to be sand (9 parts), sawdust, and non-agricultural lime (3 parts each) with Portland cement (2 parts). As the timbers are end grain, they are likely to dry and move. The suggested mix takes some time to cure, allowing for some movement.
The origins of cordwood are unclear, but structures around 1000 years old existing in Germany and other countries such as Sweden and Canada also have some tradition of employing this method. It has some advantages because it can make effective use of off-cuts and end logs, not requiring the longer timbers usually needed for framing and log construction. It is also a relatively simple and cost-effective vernacular construction method, making it popular with self-builders, and as walls often contain high quantities of mortar, it has increased thermal as well as some insulative properties. As the timbers are laid with the end grain exposed externally, the thermal properties are decreased, though this can be countered by the depth of the timbers that are used, as well as the introduction of vermiculate into the mortar mix and the potential for cavity wall construction or two layers.
While it remains not a particularly common construction method, its use of potential waste end-grain wood material from logging makes it very cost-effective. It is still an approach that is used today in many different countries. The image above is described as; a built section of cordwood masonry wall. Cut log ends protrude slightly from the pointed mortar join. Earthwood Building School, 2016. (source: cordwoodmasonry.com Author Trajinus under CC license).
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Cement mortar.
- Deforestation.
- Dry hydrate lime mortar.
- Forests.
- Grout.
- Hot-mixed lime mortar.
- Hemp lime construction: A guide to building with hemp lime composites.
- Hydraulic lime.
- Lime putty mortar.
- Lime run-off.
- Mortar.
- Mortar analysis for specifiers.
- Pointing.
- Portland cement.
- Sustainable timber.
- Sweet chestnut
- Timber species
- Types of rapidly renewable content
- The history of timber construction in the UK.
- Types of rapidly renewable content
- Types of mortar.
Featured articles and news
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this...
National Apprenticeship Week 2026, 9-15 Feb
Shining a light on the positive impacts for businesses, their apprentices and the wider economy alike.
Applications and benefits of acoustic flooring
From commercial to retail.
From solid to sprung and ribbed to raised.
Strengthening industry collaboration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong Institute of Construction and The Chartered Institute of Building sign Memorandum of Understanding.
A detailed description from the experts at Cornish Lime.
IHBC planning for growth with corporate plan development
Grow with the Institute by volunteering and CP25 consultation.
Connecting ambition and action for designers and specifiers.
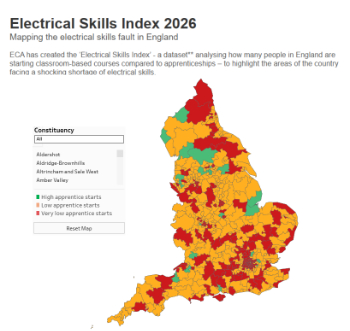
Electrical skills gap deepens as apprenticeship starts fall despite surging demand says ECA.
Built environment bodies deepen joint action on EDI
B.E.Inclusive initiative agree next phase of joint equity, diversity and inclusion (EDI) action plan.
Recognising culture as key to sustainable economic growth
Creative UK Provocation paper: Culture as Growth Infrastructure.
Futurebuild and UK Construction Week London Unite
Creating the UK’s Built Environment Super Event and over 25 other key partnerships.
Welsh and Scottish 2026 elections
Manifestos for the built environment for upcoming same May day elections.
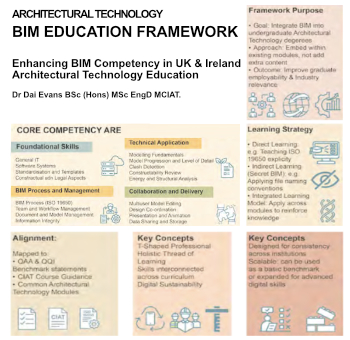
Advancing BIM education with a competency framework
“We don’t need people who can just draw in 3D. We need people who can think in data.”