Gantt chart
The timeline bar chart, Gantt diagram or Gantt chart was conceived by the American engineer Henry L. Gantt between 1903 and 1917. The basic technique is quite simple, consisting of a graphic representation based around two axes: the vertical axis features tasks and the horizontal axis shows time.
Gantt attempted to solve the activity scheduling problem so that the duration of a basic task was seen on a horizontal bar,showing its start and completion date, and in the same way the total time required in executing an activity. It is the most widespread scheduling method as it adapts well to both small and large projects of all types, assuming they are not overly complex. It is the most commonly used method of scheduling works in the construction industry and can be easily understood, even by those less familiar with scheduling tools.
The preparation of the chart may include a range of basic data spread over columns:
- Activities, according to the order in which they are carried out.
- Budget or cost.
- Quantity in its corresponding units.
- Predicted performance for working equipment.
- Duration of the activity.
The time unit used may be days (short projects), weeks (medium term projects) or months (long-term projects). The beginning and end of each horizontal bar represents the start and completion date for the corresponding task and so the length of the bar is therefore proportional to the duration. The last two rows of the chart may detail the cost or budget per unit of time in addition to that accumulated since the project began.
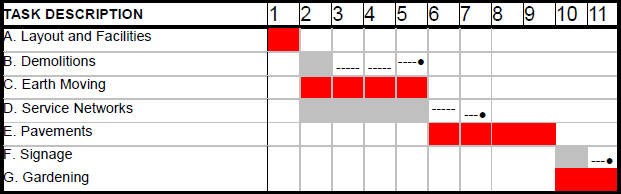
The figure below shows a simplified Gantt diagram, indicating the tasks and their monthly distribution for the first break-down level as well as the tasks which comprise the critical path and the float.
Gantt charts can be very effective in the initial planning stages, but the graphics can become confusing when changes are made and they have serious limitations for complex projects. It was these difficulties which gave rise to the development of more complex network diagrams.
The text in this article is based on an extract from CONSTRUCTION MANAGEMENT, by Eugenio Pellicer, Víctor Yepes, José M.C. Teixeira, Helder Moura and Joaquín Catala. Valencia, Porto, 2008. The original manual is part of the Construction Managers’ Library – created within the Leonardo da Vinci (LdV) project No: PL/06/B/F/PP/174014, entitled: “COMMON LEARNING OUTCOME FOR EUROPEAN MANAGERS IN CONSTRUCTION”. It is reproduced here in a modified form with the kind permission of the Chartered Institute of Building
--CIOB
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Acceleration.
- Activity schedule.
- Construction project management software.
- Contract programme.
- Contractor's master programme.
- Critical path method.
- Design web.
- Earned value.
- Information release schedules.
- Key performance indicators.
- Line of balance (LOB).
- Milestones.
- Pareto analysis.
- Precedence diagram method.
- Programme float.
- Programme consultant.
- Project crashing.
- Time-location chart.
- Time management of construction projects.
- Work breakdown structure.
[edit] External references
Featured articles and news
Homes England creates largest housing-led site in the North
Successful, 34 hectare land acquisition with the residential allocation now completed.
Scottish apprenticeship training proposals
General support although better accountability and transparency is sought.
The history of building regulations
A story of belated action in response to crisis.
Moisture, fire safety and emerging trends in living walls
How wet is your wall?
Current policy explained and newly published consultation by the UK and Welsh Governments.
British architecture 1919–39. Book review.
Conservation of listed prefabs in Moseley.
Energy industry calls for urgent reform.
Heritage staff wellbeing at work survey.
A five minute introduction.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Showcasing the very best electrotechnical and engineering services for half a century.
Welsh government consults on HRBs and reg changes
Seeking feedback on a new regulatory regime and a broad range of issues.
CIOB Client Guide (2nd edition) March 2025
Free download covering statutory dutyholder roles under the Building Safety Act and much more.
Minister quizzed, as responsibility transfers to MHCLG and BSR publishes new building control guidance.
UK environmental regulations reform 2025
Amid wider new approaches to ensure regulators and regulation support growth.
BSRIA Statutory Compliance Inspection Checklist
BG80/2025 now significantly updated to include requirements related to important changes in legislation.