Constructivist architecture
Constructivist architecture, or ‘constructivism’, is a form of modern architecture that developed in the Soviet Union in the 1920s. Inspired by the Bauhaus and the wider constructivist art movement that emerged from Russian Futurism, constructivist architecture is characterised by a combination of modern technology and engineering methods and the socio-political ethos of Communism. Despite there being few realised projects before the movement became outdated in the mid-1930s, it has had a definite influence on many subsequent architectural movements, such as Brutalism.
Following the 1917 Russian Revolution, the USSR became economically insecure and unable to embark on major construction projects. Nevertheless, avant-garde design schools began to encourage and inspire ambitious architects and urban planners, in particular the Association of New Architects (ASNOVA) which was established in 1921.
The fundamental tension of Constructivist architecture was the need to reconcile the economic reality of the USSR with its ambition for using the built environment to engineer societal changes and instil the avant-garde in everyday life. Architects hoped that through constructivism, the spaces and monuments of the new socialist utopia, the ideal of which the Bolshevik revolution had waged, could be realised.
As such, constructivist architecture was used to build utilitarian projects for the workers, as well as more creative projects such as Flying City, that was intended as a prototype for airborne housing.
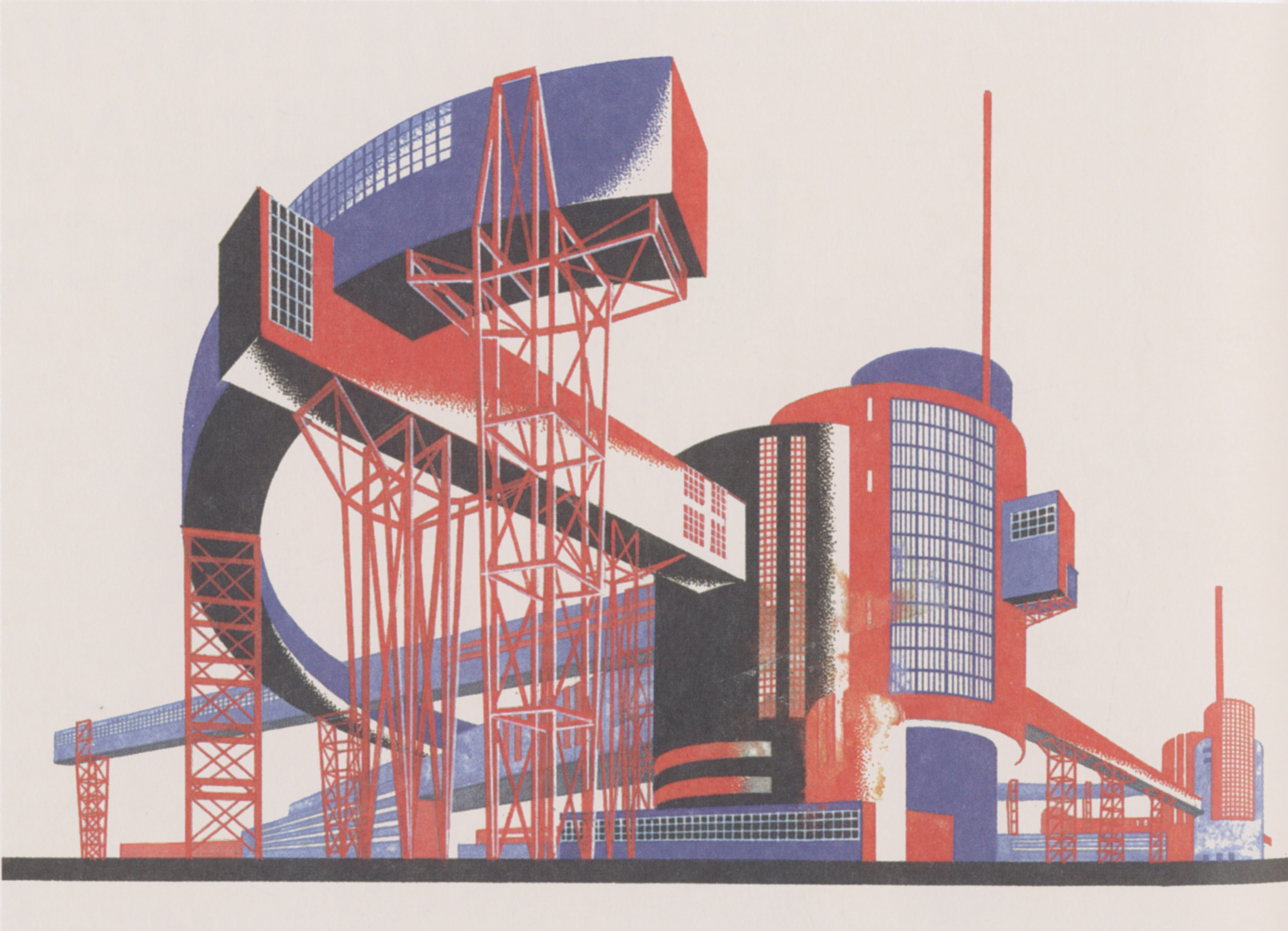
The main characteristic of constructivism was the application of 3D cubism to abstract and non-objective elements. The style incorporated straight lines, cylinders, cubes and rectangles; and merged elements of the modern age such as radio antennae, tension cables, concrete frames and steel girders. The possibilities of modern materials were also explored, such as steel frames that supported large areas of glazing, exposed rather than concealed building joints, balconies and sun decks.
The style aimed to explore the opposition between different forms as well as the contrast between different surfaces, predominately between solid walls and windows, which often gave the structures their characteristic sense of scale and presence.
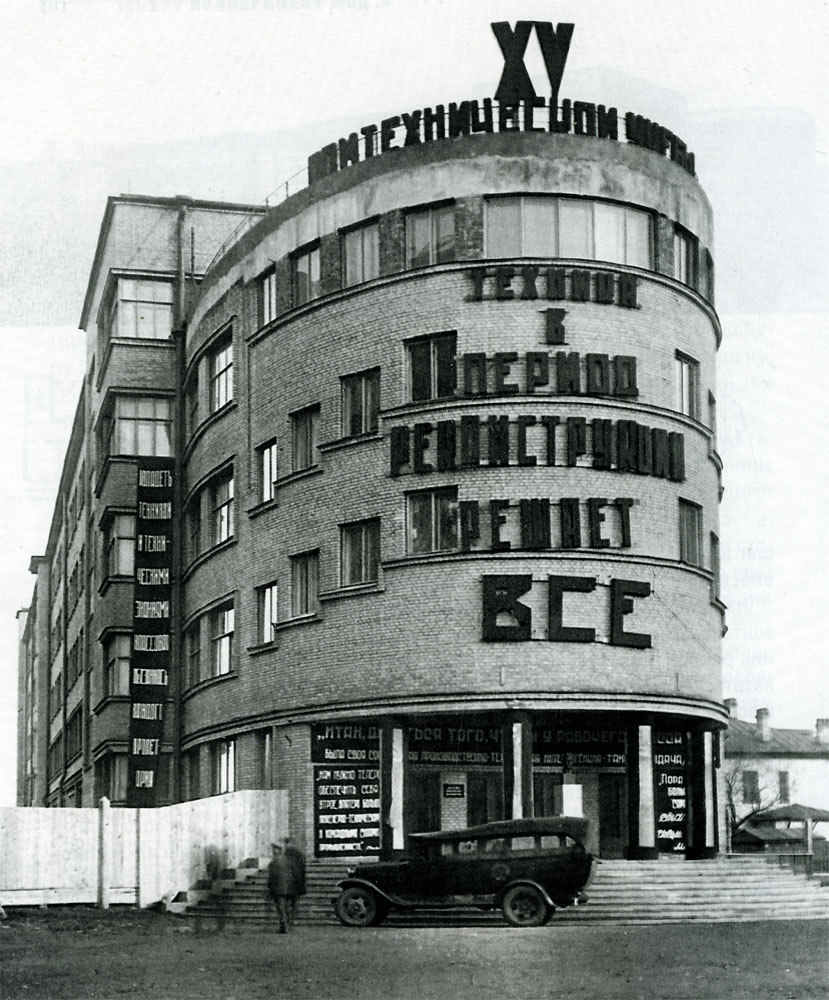
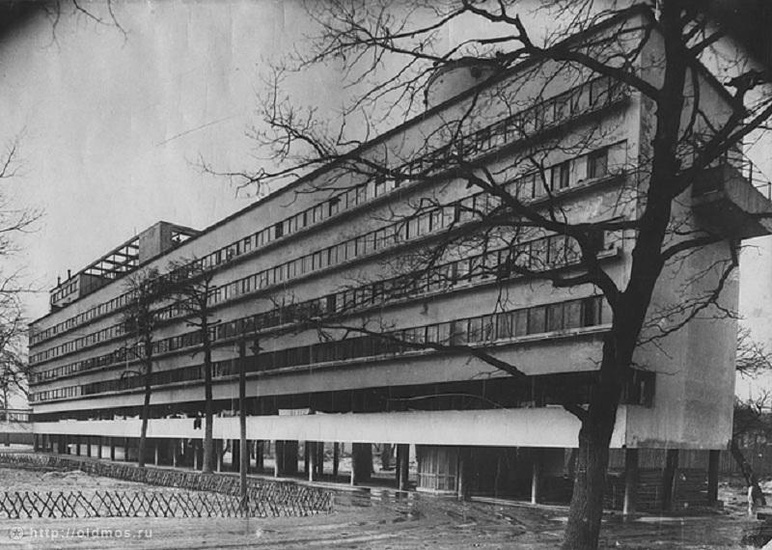
The first and perhaps most famous project was one an unrealised proposal for Tatlin’s Tower, the headquarters of the Comintern in St. Petersburg. Many subsequent, ambitious projects were not actually built, but Russia’s fourth-largest city Yekaterinburg is regarded as a ‘Constructivist museum’ including 140 built examples of the form. Another famous surviving example is the social housing project Dom Narkomfin in Moscow.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Abandoned movie theatres in Russia.
- Architectural styles.
- Art Deco.
- Art Moderne.
- Art Nouveau.
- Bauhaus.
- Brutalism.
- Concept architectural design.
- Deconstructivism.
- Expressionist architecture.
- High-tech architecture.
- Imagine Moscow exhibition.
- Megastructure.
- Metabolism.
- Mimetic architecture.
- Ministry of Transportation Building, Georgia.
- Nowa Huta - Communist tour review.
- Owen Hatherley - Landscapes of Communism.
- Skyscraper.
- Spomeniks.
[edit] External references
- Archdaily - A short history of Yekaterinburg's constructivist architecture
- World of Level Design - Constructivist architecture
Featured articles and news
The Architectural Technology podcast: Where it's AT
Catch up for free, subscribe and share with your network.
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.