Tension

|

|

|

|
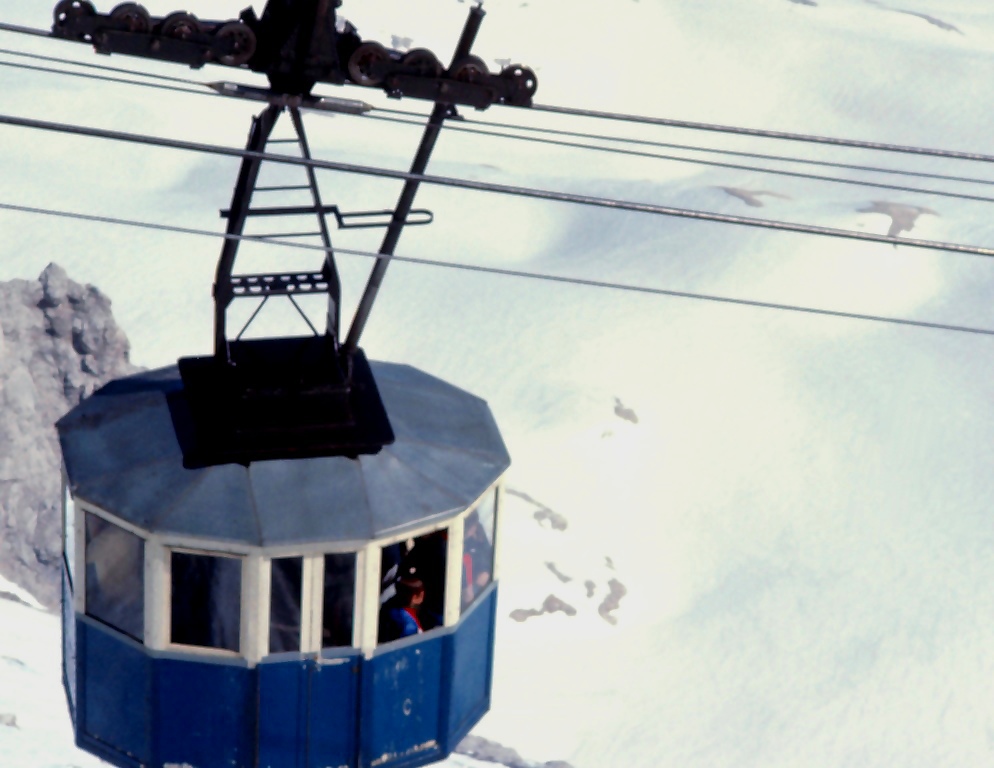
Tension is a state of stress in which a material is being pulled apart, for example a cable that is attached to a ceiling with a weight fixed to its lower end. Under the influence of gravity, the weight exerts a downward pressure that produces tension in the cable, as does the reaction at the fixing point in the ceiling.
A similar effect will be produced by two people each holding one end of a length of rope and pulling hard. Another example is a lift car that is moved by steel cables – the fibres in the cables will tend to be pulled apart by the weight of the lift car.
In both the above cases, the fibres become longer as a result of the weight applied. When a unit length of material becomes elongated, it is termed ‘tensile strain’.
As long as the cable is not stressed above its elastic range, the extent of lengthening will depend on its cross section, its length and the load applied. The larger the cable diameter, the smaller the unit elongation. Experiments have shown that elongation is inversely proportional to the area, so a member of 20mm2 cross-sectional area will stretch half the amount of a member of the same material that is 10mm2.
Hooke’s Law states that an increase in the load produces a proportionate increase in elongation and that this elongation is directly proportional to the length of the member. So, for a given load and given length of member, a member 2m-long will stretch twice as much as a 1m-long member of the same material.
In addition to elongation (the main consequence) other deformations may occur when a material is subjected to simple tension. If a material is carefully measured before and after a load is applied, it is observed that with the increase in load and the accompanying elongation, there is also an increase in diameter. This phenomenon was first observed by the French 19th century physicist Poisson.
Poisson’s ratio is the relationship between the lateral strain and horizontal strain. For steel it is around 0.33.
Tension has different effects on materials: concrete does not accommodate tensile stresses well and may crack and suffer extensive damage – with little elongation; while steel is very strong in tension and can elongate substantially under load. It is for this reason that concrete is often reinforced with steel rebar.
The opposite of tension is 'compression' which sees materials pushed or compressed together when a compressive force is applied.
Structures with tension elements include:
Three-dimensional tensile structures typically form doubly-curved shapes that are either anticlastic or synclastic.
For more information see: Tensile structures.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
The restoration of the novelist’s birthplace in Eastwood.
PAC report on the Remediation of Dangerous Cladding
Recommendations on workforce, transparency, support, insurance, funding, fraud and mismanagement.
New towns, expanded settlements and housing delivery
Modular inquiry asks if new towns and expanded settlements are an effective means of delivering housing.
Building Engineering Business Survey Q1 2025
Survey shows growth remains flat as skill shortages and volatile pricing persist.
Construction contract awards remain buoyant
Infrastructure up but residential struggles.
Home builders call for suspension of Building Safety Levy
HBF with over 100 home builders write to the Chancellor.
CIOB Apprentice of the Year 2024/2025
CIOB names James Monk a quantity surveyor from Cambridge as the winner.
Warm Homes Plan and existing energy bill support policies
Breaking down what existing policies are and what they do.
Treasury responds to sector submission on Warm Homes
Trade associations call on Government to make good on manifesto pledge for the upgrading of 5 million homes.
A tour through Robotic Installation Systems for Elevators, Innovation Labs, MetaCore and PORT tech.
A dynamic brand built for impact stitched into BSRIA’s building fabric.
BS 9991:2024 and the recently published CLC advisory note
Fire safety in the design, management and use of residential buildings. Code of practice.