Stairs riser
Part K of the building regulations requires that the rise, going, handrails, headroom, length and width of any stairs, ladders and ramps between levels are appropriate to afford reasonable safety to people gaining access to and moving about buildings.
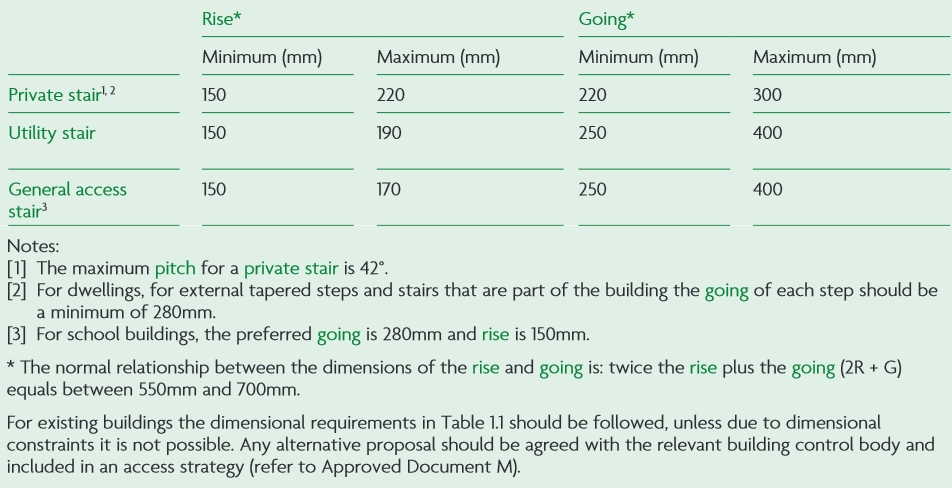
Approved Document K - Protection from falling, collision and impact describes provisions that would satisfy this requirement. It defines the ‘rise’ of stairs as the height between consecutive treads, or for ramps, the vertical distance between each end of the ramp flight.
In a flight of steps, for all steps the measurements for rise and going should be as shown below.
All buildings should have level treads on steps, with the rise and going of each step consistent throughout a flight of steps. If stairs have more than 36 risers in consecutive flights there should be a minimum of one change of direction between flights.
Buildings other than dwellings should not have single steps. For flights between landings the maximum number of risers should be 16 risers for utility stairs and for general access stairs, 12 risers, but exceptionally no more than 16 in small premises where the plan area is restricted.
In buildings other than dwellings, risers should not be open, in order to avoid feet or walking aids being caught underneath the tread during ascent, possibly causing a fall or giving occupants a feeling of insecurity. In dwellings, steps may have open risers if treads overlap by a minimum of 16 mm and steps are constructed so that a 100 mm diameter sphere cannot pass through the open risers.
In buildings other than dwellings, step nosings should be made apparent using a visually contrasting material, a minimum of 55 mm wide, on both the tread and the riser. For common access areas in buildings that contain flats, risers should not be open and step nosings should be visually apparent, using a material that contrasts visually, 50 - 65 mm wide on the tread and 30 - 55 mm on the riser.
Where there are stepped gangways in assembly buildings, each step in the gangway should have a minimum height of 100 mm and a maximum height of 190 mm. If there are two or more rises to each row of seats, each step should be of an equal height.
See also: Stair rise.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
Homes England creates largest housing-led site in the North
Successful, 34 hectare land acquisition with the residential allocation now completed.
Scottish apprenticeship training proposals
General support although better accountability and transparency is sought.
The history of building regulations
A story of belated action in response to crisis.
Moisture, fire safety and emerging trends in living walls
How wet is your wall?
Current policy explained and newly published consultation by the UK and Welsh Governments.
British architecture 1919–39. Book review.
Conservation of listed prefabs in Moseley.
Energy industry calls for urgent reform.
Heritage staff wellbeing at work survey.
A five minute introduction.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Showcasing the very best electrotechnical and engineering services for half a century.
Welsh government consults on HRBs and reg changes
Seeking feedback on a new regulatory regime and a broad range of issues.
CIOB Client Guide (2nd edition) March 2025
Free download covering statutory dutyholder roles under the Building Safety Act and much more.
Minister quizzed, as responsibility transfers to MHCLG and BSR publishes new building control guidance.
UK environmental regulations reform 2025
Amid wider new approaches to ensure regulators and regulation support growth.
BSRIA Statutory Compliance Inspection Checklist
BG80/2025 now significantly updated to include requirements related to important changes in legislation.