Types of stairs

|
|
|

|
Contents[hide] |
[edit] Introduction
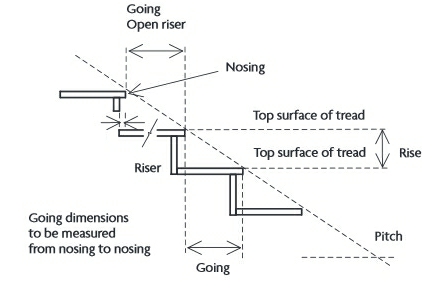
Stairs are used to create a pedestrian route between different vertical levels by dividing the height between the levels into manageable steps. Very generally, the word 'stairs' refers to a staircase, whereas the word 'step' refers to the steps that make up the staircase.
The type of stairs suitable for different situations will depend on:
- The supporting structure.
- The amount and type of usage it is likely to receive.
- The space available and its geometry.
- The difference in height between the top and bottom.
- Materials selection
Stairs may be:
- Open tread or closed tread.
- Provided with handrails on one or both sides, or in the middle on wide stairs.
- Enclosed by walls or open on one or both side.
- Different widths and lengths and may have a range of step dimensions.
- Different geometries.
[edit] Geometries
Some of the most common types of stair geometry include:
[edit] Straight
Generally the most prevalent type of stairs, straight stairs comprise a single linear flight which does not change direction.
Where there are more than 36 risers in consecutive flights of stairs, Approved Document K requires that there is at least one change of direction, with a landing that has a minimum length equal to the width of the stairs.
[edit] Quarter-turn
Quarter-turn, or L-shaped, stairs comprise a straight flight of stairs that makes a 90-degree turn after a landing. This type can be considered safer than a straight staircase since the landing reduces the number of treads in one flight and provides a place to rest.
[edit] Winder
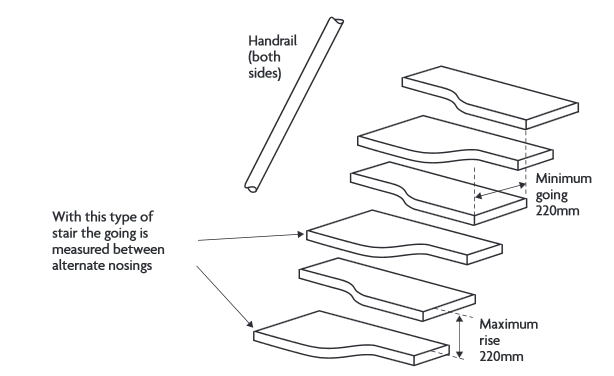
This type of stairs is similar to a quarter-turn staircase, but consists of winders which are wedge-shaped treads, wider on one side than the other. Winders allow a turn by 90-degrees (single winder) or 180-degrees (double winder).
For more information see: Winder.
[edit] Half-turn
Half-turn, or U-shaped, stairs comprise two straight flights of stairs that make a 180-degree turn having been separated by a landing.
[edit] Spiral
This type of stair is a compact design with flights resembling a circle (or part of a circle), and centred around a single vertical column. Similar to winder stairs, the treads are wedge-shaped but differ in that they are all uniformly sized (except the final one).
Although spiral stairs are often considered to be aesthetically pleasing and effective in terms of space, they may not be the most convenient in terms of frequent use as the treads can often be less easy or safe to traverse than other types of stairs.
[edit] Helical
A helical stair similar to a spiral stair, but the helix wraps around a central void rather than a column.
[edit] Curved
Also known as arched stairs, this type of stair comprises a continuous flight that is shaped like an arch, with no landings. The treads are wedge-shaped similar to winder stairs. Although achieving an elegant aesthetic, curved stairs are difficult to construct since all basic details, banisters, and so on, need to be curved.
[edit] Bifurcated
Bifurcated stairs comprise a grand and sweeping set of stairs that divides into two smaller flights that split off into opposite directions.
[edit] Compact
This type of stairs, also known as narrow stairs, are often designed as a solution to confined space within a building. They comprise distinctive treads that are designed to take one foot only.
[edit] Alternating tread
A stair with paddle-shaped treads where the wide portion is on alternate sides on consecutive treads. On older stairs, they tread may sometimes just alternate from one side to the other. This is sometimes referred to as a 'witches stair' because of the belief that witches were unable to climb them.
[edit] Uses
Different types of stair use include:
[edit] Utility stair
Approved document K defines a 'utility stair' as '...a stair used for escape, access for maintenance, or purposes other than as the usual route for moving between levels on a day-to-day basis.'
[edit] General access stair
Approved document K defines a 'general access stair' as '...a stair intended for all users of a building on a day-to-day basis, as a normal route between levels.'
[edit] Private stair
Approved document K defines a 'private stair' as '...a stair intended to be used for only one dwelling'
[edit] Protected stair
Approved document B defines a ‘protected stair’ as ‘…a stair discharging through a final exit to a place of safety (including any exit passageway between the foot of the stair and the final exit) that is adequately enclosed with fire resisting construction’.
See: Protected stairway for more information.
[edit] Firefighting stair
Approved document B defines a ‘firefighting stair’ as ‘… a protected stairway communicating with the accommodation area through a firefighting lobby’.
[edit] Common stair
Approved document B defines a ‘common stair’ as ‘… an escape stair serving more than one flat’.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
Gregor Harvie argues that AI is state-sanctioned theft of IP.
Preserving, waterproofing and decorating buildings.
Many resources for visitors aswell as new features for members.
Using technology to empower communities
The Community data platform; capturing the DNA of a place and fostering participation, for better design.
Heat pump and wind turbine sound calculations for PDRs
MCS publish updated sound calculation standards for permitted development installations.
Homes England creates largest housing-led site in the North
Successful, 34 hectare land acquisition with the residential allocation now completed.
Scottish apprenticeship training proposals
General support although better accountability and transparency is sought.
The history of building regulations
A story of belated action in response to crisis.
Moisture, fire safety and emerging trends in living walls
How wet is your wall?
Current policy explained and newly published consultation by the UK and Welsh Governments.
British architecture 1919–39. Book review.
Conservation of listed prefabs in Moseley.
Energy industry calls for urgent reform.
Heritage staff wellbeing at work survey.
A five minute introduction.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Showcasing the very best electrotechnical and engineering services for half a century.
Welsh government consults on HRBs and reg changes
Seeking feedback on a new regulatory regime and a broad range of issues.























