Stairs tread
Regulations for the design and construction of stairs are set out in Part K of the building regulations, and compliant designs are described in Approved Document K - Protection from falling, collision and impact.
The treads of stairs are the horizontal parts which people step on.
The leading edge of the tread is described as the ‘nosing’. In buildings other than dwellings, the nosing should be visually contrasting, and a suitable tread nosing profile, should be used. See nosing for more information.
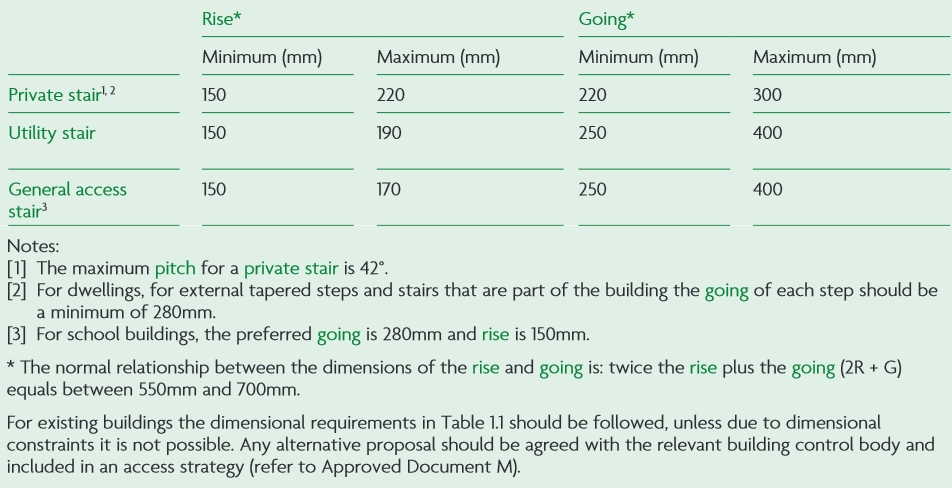
Steps should have level treads with the rise and going of each step consistent throughout a flight of steps and are in accordance with the table below.
In buildings other than dwellings, risers should not be open to avoid feet or walking aids being caught underneath the tread during ascent, possibly causing a fall or giving occupants a feeling of insecurity. For dwellings, steps may have open risers if treads overlap by a minimum of 16 mm and steps are constructed so that a 100 mm diameter sphere cannot pass through the open risers.
A tapered tread is a step in which the going reduces from one side to the other. Where stairs have tapered treads, consecutive treads should use the same going. If a stair consists of straight and tapered treads, the going of the tapered treads should not be less than the going of the straight treads.
Alternating tread stairs are stairs with paddle-shaped treads where the wide portion is on alternate sides on consecutive treads. In dwellings, alternating tread stairs may only be used in loft conversions where there is not enough space for conventional stairs and where the stair is for access to only one habitable room and, if desired, a bathroom and/or a WC (although this must not be the only WC in the dwelling).
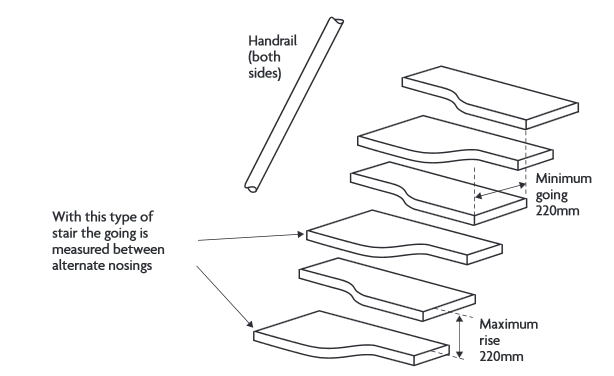
Alternating tread stairs should; make alternating steps uniform with parallel nosings, have slip-resistant surfaces on treads, have tread sizes over the wider part of the step in line with the table above, should provide a minimum clear headroom of 2 m, should be constructed so that a 100 mm diameter sphere cannot pass through the open risers and should comply with the diagram below.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
British architecture 1919–39. Book review.
Conservation of listed prefabs in Moseley.
Energy industry calls for urgent reform.
Heritage staff wellbeing at work survey.
A five minute introduction.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Showcasing the very best electrotechnical and engineering services for half a century.
Welsh government consults on HRBs and reg changes
Seeking feedback on a new regulatory regime and a broad range of issues.
CIOB Client Guide (2nd edition) March 2025
Free download covering statutory dutyholder roles under the Building Safety Act and much more.
AI and automation in 3D modelling and spatial design
Can almost half of design development tasks be automated?
Minister quizzed, as responsibility transfers to MHCLG and BSR publishes new building control guidance.
UK environmental regulations reform 2025
Amid wider new approaches to ensure regulators and regulation support growth.
The maintenance challenge of tenements.
BSRIA Statutory Compliance Inspection Checklist
BG80/2025 now significantly updated to include requirements related to important changes in legislation.
Shortlist for the 2025 Roofscape Design Awards
Talent and innovation showcase announcement from the trussed rafter industry.
OpenUSD possibilities: Look before you leap
Being ready for the OpenUSD solutions set to transform architecture and design.
Global Asbestos Awareness Week 2025
Highlighting the continuing threat to trades persons.
Retrofit of Buildings, a CIOB Technical Publication
Now available in Arabic and Chinese as well as English.