Specularia
The term specularia, is often used to describe a small genus of annual herbs, however it can also be used in reference to the Latin meaning of letting light in or transparency. Lapis specularis is also used to describe the selenite crystal form of gypsum (selenitic) that forms in thin sheets. Specularis might be used to describe to a mirroring quality. Other references refer to specularium as the Latin nominative case to mean a window-pane, transparency, or a piece of glass letting through light into a building (specularum, also has historical references to a watchtower or light house).
Specularia appears in two surviving Roman texts: Historia Naturalis, referenced by the Roman agricultural savant Pliny the Elder who describes “beds mounted on wheels which they moved out into the sun and then on wintry days withdrew under the cover of frames, glazed with transparent stone or mica to provide fruits of cucumis.” The second De Re Rustica (On Agriculture) by Columella goes further recommending siting near buildings for wind protection and warmth for the beds.
Many years later in the 1500's the purpose of these devices was described; “The young plants may be defended from cold and boisterous windes, yea, frosts, the cold aire, and hot Sunne, if Glasses made for the onely purpose, be set over them, which on such wise bestowed on the beds, yeelded in a manner to Tiberius Caesar, Cucumbers all the year, in which he took great delight...” (Thomas Hill, “The Gardener’s Labyrinth”, 1577).
In 2010 in the paper; What the Roman emperor Tiberius grew in his greenhouse and in 2022 article History of Controlled Environment Horticulture: Ancient Origins both by H.S. Paris and J. Janick, it is argued that it was actually melons (Cucumis melo) that were grown, ones that lacked sweetness, rather than cucumbers (Cucumis sativus) as described by Hill, describing more specifically the details and other varieties of plants grown in these early greenhouses.
In any case the purpose of these greenhouses was to prolong the growing season for the crop which according to Pliny “a delicacy for which the Emperor Tiberius (reigning from 42 BCE-37 CE), had a remarkable partiality; in fact there was never a day on which he was not supplied it.” Other references talk of specularium and specularia as buildings or early green houses made on the same principles, just static, though this is not clear in history, even if the material was.
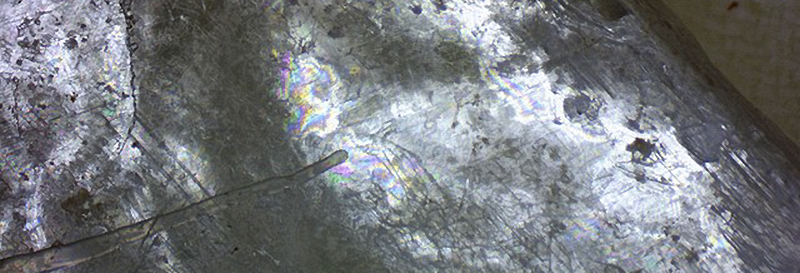
The material used is sometimes described as being mica, which is any of the group of hydrous aluminosilicate minerals which form in layers, more specifically it is likely to have been Lapis Specularis the form of Selenite or naturally pure crystalline gypsum. Selenite crystals form in large flat, transparent crystals, often called plates or windows and although at this time the Romans were able to produce glass it was not developed enough for panes as such and only used for small jewellery items and beads. It was around 100AD that Romans, by then adept at glass blowing, started to blow flattened glass tubes, which were then effectively cut in half to create the first window panes.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Botanical gardens
- Biomes.
- Building an extension.
- Conservatory.
- Garden greenhouse.
- Hydroponics and buildings.
- Selenite.
- Satin spar.
- The secret life of the Georgian garden.
- Types of glass.
- Winter gardens.
[edit] External References
Featured articles and news
Gregor Harvie argues that AI is state-sanctioned theft of IP.
Preserving, waterproofing and decorating buildings.
Many resources for visitors aswell as new features for members.
Using technology to empower communities
The Community data platform; capturing the DNA of a place and fostering participation, for better design.
Heat pump and wind turbine sound calculations for PDRs
MCS publish updated sound calculation standards for permitted development installations.
Homes England creates largest housing-led site in the North
Successful, 34 hectare land acquisition with the residential allocation now completed.
Scottish apprenticeship training proposals
General support although better accountability and transparency is sought.
The history of building regulations
A story of belated action in response to crisis.
Moisture, fire safety and emerging trends in living walls
How wet is your wall?
Current policy explained and newly published consultation by the UK and Welsh Governments.
British architecture 1919–39. Book review.
Conservation of listed prefabs in Moseley.
Energy industry calls for urgent reform.
Heritage staff wellbeing at work survey.
A five minute introduction.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Showcasing the very best electrotechnical and engineering services for half a century.
Welsh government consults on HRBs and reg changes
Seeking feedback on a new regulatory regime and a broad range of issues.
























Comments
[edit] To make a comment about this article, click 'Add a comment' above. Separate your comments from any existing comments by inserting a horizontal line.