Special educational needs: an analysis of the necessities for inclusion

|
| This article was written by Simone Gray, City College Plymouth. It was ‘highly commended’ in CIAT’s 2018 AT Awards in the category Student Award for Excellence in Architectural Technology (Report). The article first appeared in CIAT’s Autumn 2018 AT Journal. |
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Simone Gray writes: “One of the modules I had to undertake as part of my foundation degree in Construction was ‘Research Project’. For this I had to write a mini dissertation: the decision to look at SEN facilities in schools came after seeing the struggles my parents went through trying to find a suitable school for my younger brother who has been diagnosed with autism. The limited number of schools with special education needs places in Plymouth made me question why all schools, especially new ones being built, were not to a standard that would be acceptable for students such as my brother.”
[edit] Designing for children with special educational needs
The report itself is a study of the main elements that need to be incorporated into a mainstream school that are necessary for the inclusion of children with special educational needs. To find out what those main features were and to determine end-user requirements, a study was undertaken by carrying out questionnaires of different teaching professionals along with semi-structured interviews of two schools in Plymouth.
Once the highest impacting elements were discovered, they were critically analysed and the report finishes with suggested guidelines for how to create a mainstream school that would be inclusive to all students.
The features that were investigated further included: classroom layout and acoustics, facilities such as hygiene and learning resource areas, and outdoor space.
It was concluded that the layout of a classroom is important due to the impact it has on how a child feels, functions and learns within that environment. There is a need for classrooms to be large enough to ensure accessibility to all students, and the use of zoned areas to break-up space to ensure ease of use and understanding of activities for the end user. Conclusions were drawn from the results of the questionnaires and interviews along with constant reference to government-approved guidelines to ensure that any recommendations would be compliant. Illustrations were used within the report to give examples of different design proposals and examples of feedback received, such as visual timetables.
The acoustics of a classroom were analysed with both technical and aesthetic aspects in mind. Published guidelines were used to determine the correct indoor ambient noise level and reverberation times of an ‘ideal’ classroom. These levels are important in a learning environment to ensure clear speech intelligibility and an ambient noise level that suites the end user. SEN pupils are more sensitive to sound and therefore require shorter reverberation times, and lower indoor ambient noise levels. Reverberation times can be controlled with the use of acoustic absorption materials.
These materials are graded A to E, with ‘A’ being highly absorbent and ‘E’ almost fully reflective. The absorbent materials can come in different forms including ceiling tiles, acoustic beams/ceiling panels, wall panels, and perforated/slatted wooden ceiling strips. Acoustic panels can also be used for aesthetic purposes as they can be produced in a wide range of colours, shapes, sizes or patterns. However, depending on the end use, this may cause too much of a distraction but this can be decided at the design stage.
When analysing facilities, care was taken to consider the recommendations received from the teaching professionals who undertook the questionnaire, including clear labelling, easy access and the need for space and discretion when required. However, most conclusions for hygiene and toilet facilities came from information published within government guidelines, including BB104 and Approved Document M to ensure that all design proposals were compliant.
[edit] Outdoor space
Outdoor space was the final area that was reviewed, with studies identifying benefits that can help develop and grow children with SEN. Having the ability to take a classroom outside, for exploration and learning can be sensory inspiring, especially when combining natural stimulators like wind, grass and trees with play equipment. A multi-sensory environment can promote interaction, communication, overcome boredom, reduce stress and relieve excess energy that a lot of SEN children have. Sandpits, musical instruments, play equipment and planting beds combined can create a natural, sensory outdoor space for teaching and play.
Along with these design considerations, children need a small transition area between leaving the classroom and entering outdoor space. Many children with SEN struggle with change and making the transition a smoother, simpler process will reduce stress and anxiety for the child. Having a covered outside space also means children can still attend outdoor classes when the weather is not good.
If all of these design elements were incorporated into compulsory guidelines when designing a mainstream school, more children with autism and other additional needs would not feel isolated and would receive the education they deserve and need. Social interaction, communication and relationships could be improved, meaning that the school life of 1,244,255 pupils could be improved.
[edit] Judge’s comments
This research focused upon inclusivity and wellbeing linked to special-need facilities and the design of spaces for people who would benefit from such an environment. An interesting subject area – academic and well researched with good context and clear aims and objective. A very relevant topic with thorough analysis, well presented and clearly illustrated. The section on acoustics is the most developed and technically relevant section.
This article was written by Simone Gray, City College Plymouth. It was ‘highly commended’ in CIAT’s 2018 AT Awards in the category Student Award for Excellence in Architectural Technology (Report). The article first appeared in CIAT’s Autumn 2018 AT Journal.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Access and inclusion in the built environment: policy and guidance
- Accessible London: Achieving an Inclusive Environment SPG
- Baseline designs for schools
- BREEAM Visual comfort View out
- Building Bulletin 93: acoustic design of schools.
- Building regulations
- Inclusive design
- Inclusive Environments, Built Environment Industry Action Plan
- People with disabilities definition
--CIAT
Featured articles and news
CLC and BSR process map for HRB approvals
One of the initial outputs of their weekly BSR meetings.
Building Safety Levy technical consultation response
Details of the planned levy now due in 2026.
Great British Energy install solar on school and NHS sites
200 schools and 200 NHS sites to get solar systems, as first project of the newly formed government initiative.
600 million for 60,000 more skilled construction workers
Announced by Treasury ahead of the Spring Statement.
The restoration of the novelist’s birthplace in Eastwood.
Life Critical Fire Safety External Wall System LCFS EWS
Breaking down what is meant by this now often used term.
PAC report on the Remediation of Dangerous Cladding
Recommendations on workforce, transparency, support, insurance, funding, fraud and mismanagement.
New towns, expanded settlements and housing delivery
Modular inquiry asks if new towns and expanded settlements are an effective means of delivering housing.
Building Engineering Business Survey Q1 2025
Survey shows growth remains flat as skill shortages and volatile pricing persist.
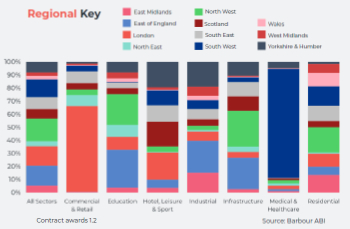
Construction contract awards remain buoyant
Infrastructure up but residential struggles.
Home builders call for suspension of Building Safety Levy
HBF with over 100 home builders write to the Chancellor.
CIOB Apprentice of the Year 2024/2025
CIOB names James Monk a quantity surveyor from Cambridge as the winner.
Warm Homes Plan and existing energy bill support policies
Breaking down what existing policies are and what they do.
Treasury responds to sector submission on Warm Homes
Trade associations call on Government to make good on manifesto pledge for the upgrading of 5 million homes.
A tour through Robotic Installation Systems for Elevators, Innovation Labs, MetaCore and PORT tech.
A dynamic brand built for impact stitched into BSRIA’s building fabric.
BS 9991:2024 and the recently published CLC advisory note
Fire safety in the design, management and use of residential buildings. Code of practice.