Flood Resistant Construction
A flood resistant building is one that is designed to resist flood water ingress. That means that the building is designed to prevent flood water from entering through the walls, floor and any apertures. The deeper the flood water and the higher the velocity, the more difficult it is to keep water out. As water rises on the outside of the building it creates a force on the ground floor and outside walls including any windows and doors at that level.
Flood resistant buildings are typically constructed using concrete or steel and concrete but may also be made with masonry provided there is an impervious layer, such as water-resistant render or asphalt. Typically, frame buildings are more difficult to make flood resistant without a concrete or masonry layer due to the number of potential pathways for water around junctions. Masonry is generally permeable, as is concrete unless to a certain specification. Therefore, water can seep through walls and floors unless designed properly. Cavity walls may need to be filled with water resistant insulation below the flood level to prevent the passage of water and to prevent contamination within the cavity.
The ground floor is a potential pathway for floodwater to enter, particularly if flood water remains present outside for a period of time. This is because the water will seek to reach an equilibrium inside and outside the building. If the pressure from the rising water is substantial it will apply an upward force to the floor potentially causing structural damage, water penetration or the floor to rise, particularly if light.
Concrete floors may need to be reinforced to prevent the risk of fracture from the water pressure. Beam and block floors are likely to require additional waterproofing to prevent water ingress. The membrane is also likely to need to be weighed down to prevent it being forced up by the water.
Where flood depths can be greater than a few hundred millimetres (in the order of 0.5m) it may become expensive to make a building resistant to floodwater. In this case it may be more cost effective to make a building resilient to flooding. This may also be more appropriate for existing buildings.
Because most doors and windows would not prevent the ingress of water, specialist flood resistant doors and windows are required, or flood barriers located infront of ordinary doors and windows.
Special care and attention to the detailing of jambs and thresholds is required to prevent water ingress and to ensure the integrity is maintained under the pressure of water.
Where floodwater is likely to remain for several days, such as areas with relatively flat topography, it may be better to consider flood resilient construction, to reduce the reliance on the structural and waterproofing measures.
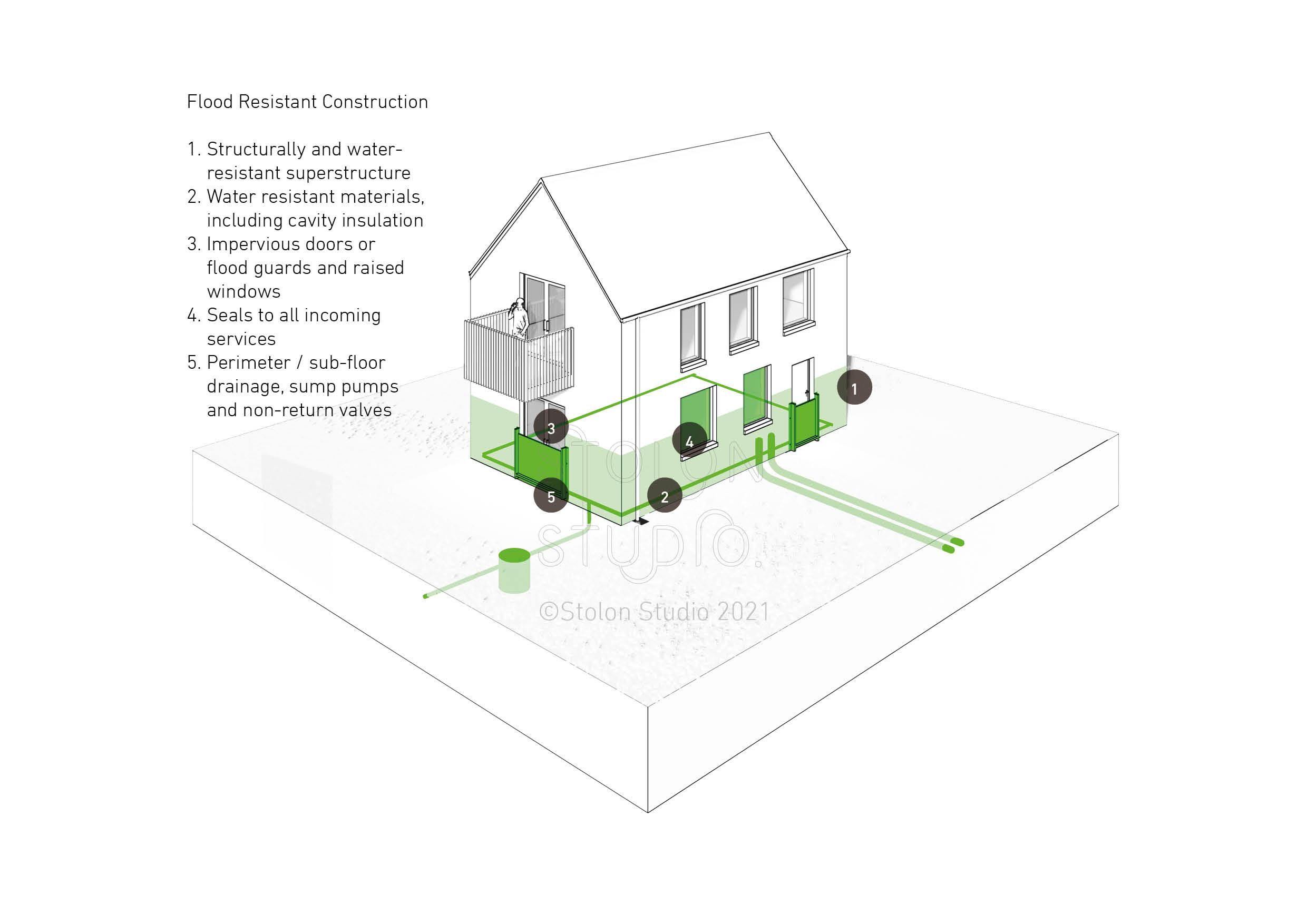
The key components of flood resistant construction are:
- Structurally and water-resistant superstructure
- Water resistant materials, including cavity insulation
- Impervious doors or flood guards and raised windows
- Seals to all incoming services
- Perimeter / sub-floor drainage, sump pumps and non-return valves
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Amphibious construction.
- BRE flood resilient repair project.
- BREEAM Flood risk management.
- Building flood resilience.
- Changing attitudes to property flood resilience in the UK.
- Elevated Construction.
- Fighting flooding in the 21st century.
- Flood defences.
- Flood resilient house.
- Pitt Review Lessons learned from the 2007 floods.
- Planning for floods.
- Property flood resilience.
- Pumps and dewatering equipment.
- Temporary flood defences.
- Ten years on - Lessons from the Flood on building resilience.
- Thames barrier.
- Workplace design – flood protection.
--Robert Barker, Stolon 23:48, 02 Nov 2021 (BST)
Featured articles and news
ECA progress on Welsh Recharging Electrical Skills Charter
Working hard to make progress on the ‘asks’ of the Recharging Electrical Skills Charter at the Senedd in Wales.
A brief history from 1890s to 2020s.
CIOB and CORBON combine forces
To elevate professional standards in Nigeria’s construction industry.
Amendment to the GB Energy Bill welcomed by ECA
Move prevents nationally-owned energy company from investing in solar panels produced by modern slavery.
Gregor Harvie argues that AI is state-sanctioned theft of IP.
Heat pumps, vehicle chargers and heating appliances must be sold with smart functionality.
Experimental AI housing target help for councils
Experimental AI could help councils meet housing targets by digitising records.
New-style degrees set for reformed ARB accreditation
Following the ARB Tomorrow's Architects competency outcomes for Architects.
BSRIA Occupant Wellbeing survey BOW
Occupant satisfaction and wellbeing tool inc. physical environment, indoor facilities, functionality and accessibility.
Preserving, waterproofing and decorating buildings.
Many resources for visitors aswell as new features for members.
Using technology to empower communities
The Community data platform; capturing the DNA of a place and fostering participation, for better design.
Heat pump and wind turbine sound calculations for PDRs
MCS publish updated sound calculation standards for permitted development installations.
Homes England creates largest housing-led site in the North
Successful, 34 hectare land acquisition with the residential allocation now completed.
Scottish apprenticeship training proposals
General support although better accountability and transparency is sought.
The history of building regulations
A story of belated action in response to crisis.
Moisture, fire safety and emerging trends in living walls
How wet is your wall?
Current policy explained and newly published consultation by the UK and Welsh Governments.
British architecture 1919–39. Book review.
Conservation of listed prefabs in Moseley.
Energy industry calls for urgent reform.