Data analytics

|
Analytics is a method which uses logical analysis to interpret large quantities of data to help with prediction and decision making. The analysis of data may include discerning trends and patterns, their interpretation and communication. Analytics is therefore the link between the data and making informed decisions. Organisations can use analytics to gain a predictive intelligence that can help shape their future plans.
Data used for analytics can be structured or unstructured. Structured data, for example, might be formatted into a table; whereas unstructured data cannot be tabulated e.g some documents or hearsay.
There are two main types of data:
- Descriptive data – this is data which describes things in the past e.g customer records, past performance, purchase history etc.
- Predictive data – this is closely linked to machine learning and looks at the future, and how to make predictions based on past events.
Once descriptive data has been gathered, it can be processed by algorithms (mathematical formulas or models) to create a model that identifies relationships in variables existing in the data and allows predictions to be made. Uncertain data for which the answers are not known e.g the type of goods that certain people in a geographical area might be interested in, can then be fed into the model which subsequently outputs what their preferences might be. This can then be reported or communicated in various formats such as tables, bar and line charts, etc.
The important result of the process is the creation of the model. Once established, data can be inputted to produce a prediction. This is the basis of machine learning which can lead to the attainment of artificial intelligence (AI).
Data analytics is useful in all walks of life but particularly in marketing where possible future consumer preferences can be predicted and therefore accommodated in campaigns. It can blend into performance analytics which may help a company measure its progress toward specific goals and to determine which actions will help achieve them.
Data analytics can be used for digital management to help construction firms to win projects and deliver them more efficiently. This is particularly apposite for large capital projects, for example, providing analysis to challenge trends in low-performance, getting a better understanding of project performance, root causes and prioritising daily activities.
Analytics will become increasingly important with the growth of big data, the internet of things and the use of sensors in the built environment.
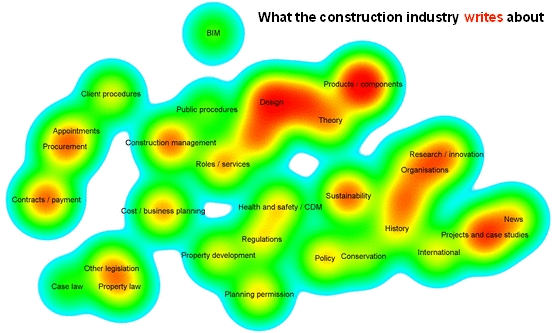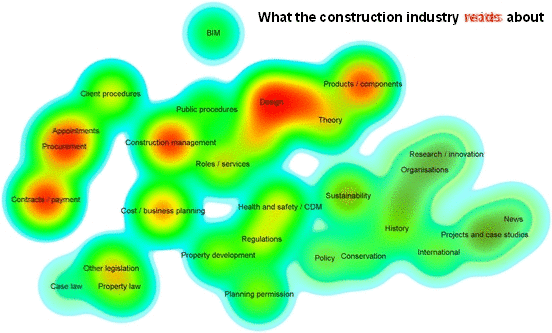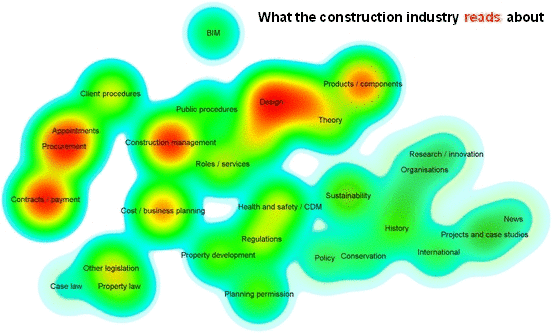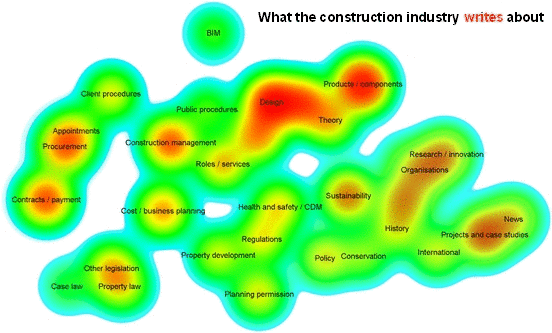
Analyics were used by Designing Buildings Wiki to assess the relationships between subjects on the website, and the difference between what authors write about and what users read about. For more information see: Fit for purpose - Big data reveals the construction knowledge gap
NB PwC Global, Digital procurement survey 2022, defines Data analytics as: ‘…the science of analyzing raw data to make conclusions about that information.’
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Asset information model.
- Big data.
- Building data exchange.
- Clustering.
- Common data environment.
- Data-centric business model.
- Data-driven mobility.
- Data and behaviours in construction.
- Data and infrastructure productivity.
- Data collection strategies.
- Data drop.
- Data manager.
- How data can stop waste.
- Interoperability.
- Internet of things.
- Making the most of big data.
- Open data - how can it aid the development of the construction industry?
- Predictive analytics.
- Procurement analytics.
- Top big data tools used to store and analyze data.
- Treating data as part of infrastructure
- Virtual reality and big data disrupting digital construction.
Featured articles and news
Homes England creates largest housing-led site in the North
Successful, 34 hectare land acquisition with the residential allocation now completed.
Scottish apprenticeship training proposals
General support although better accountability and transparency is sought.
The history of building regulations
A story of belated action in response to crisis.
Moisture, fire safety and emerging trends in living walls
How wet is your wall?
Current policy explained and newly published consultation by the UK and Welsh Governments.
British architecture 1919–39. Book review.
Conservation of listed prefabs in Moseley.
Energy industry calls for urgent reform.
Heritage staff wellbeing at work survey.
A five minute introduction.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Showcasing the very best electrotechnical and engineering services for half a century.
Welsh government consults on HRBs and reg changes
Seeking feedback on a new regulatory regime and a broad range of issues.
CIOB Client Guide (2nd edition) March 2025
Free download covering statutory dutyholder roles under the Building Safety Act and much more.
Minister quizzed, as responsibility transfers to MHCLG and BSR publishes new building control guidance.
UK environmental regulations reform 2025
Amid wider new approaches to ensure regulators and regulation support growth.
BSRIA Statutory Compliance Inspection Checklist
BG80/2025 now significantly updated to include requirements related to important changes in legislation.