Anthropometrics in architectural design
Contents[hide] |
[edit] What is anthropometrics?
Anthropometrics is the comparative study of the measurements and capabilities of the human body. It derives from the Greek words 'anthropos' (meaning human), and 'metron' (meaning measure).
Anthropometry influences a wide range of industries, processes, services and products and has a considerable importance in optimising the design of buildings.
[edit] How does anthropometrics influence building design?
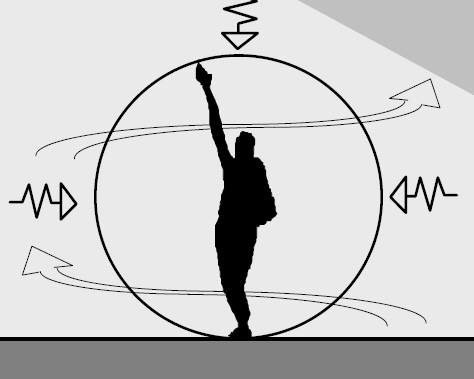
Human dimensions and capabilities are paramount in determining a building's dimensions and overall design. The underlying principle of anthropometrics is that building designs should adapt to suit the human body, rather than people having to adapt to suit the buildings.
There are two basic areas of anthropometry:
- Static anthropometry is the measurement of body sizes at rest and when using devices such as chairs, tables, beds, mobility devices, and so on.
- Functional anthropometry is the measurement of abilities related to the completion of tasks, such as reaching, manoeuvring and motion, and other aspects of space and equipment use.
The use of anthropometrics in building design aims to ensure that every person is as comfortable as possible. In practical terms, this means that the dimensions must be appropriate, ceilings high enough, doorways and hallways wide enough, and so on. In recent times, it has come to have particular significance for workplace design, and the relationship between desk, chair, keyboard and computer display.
Anthropometry may also impact on space requirements for furniture and fittings. For example, a bathroom must have enough space to comfortably fit a bath and sink; a bedroom must have enough space to comfortably fit an average-sized bed; an office building must have enough space to fit desks, air-conditioning units, communal areas, meeting rooms, and so on.
See also: Ergonomics.
[edit] Anthropometrics and inclusive design
The building regulations provide a range of standard requirements and approved solutions for designers to help develop suitable designs. However, it is important to consider the specific purpose and requirements of end users. Attempts to apply standardised dimensions may not reflect the true need of the space requirements.
Older people, children, people with mobility issues, wheelchair users and so on may have specific requirements. In particular, good accessibility and easy manoeuvrability around the building must be considered when designing stairs, lifts, ramps and other features. See Accessibility in the built environment for more information.
Anthropometric data is regularly updated to reflect changes in the population.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Accessibility in the built environment.
- Building spaces definition.
- Changing lifestyles.
- Concept architectural design checklist.
- Design intent.
- Design management for construction projects.
- Design responsibility matrix.
- Ergonomics in construction.
- Facilities management.
- Headroom.
- Inclusive design.
- Lifts.
- People with disabilities.
- Ramps.
- Scale.
- Skeuomorphism.
Featured articles and news
Gregor Harvie argues that AI is state-sanctioned theft of IP.
Experimental AI housing target help for councils
Experimental AI could help councils meet housing targets by digitising records.
New-style degrees set for reformed ARB accreditation
Following the ARB Tomorrow's Architects competency outcomes for Architects.
BSRIA Occupant Wellbeing survey BOW
Occupant satisfaction and wellbeing tool inc. physical environment, indoor facilities, functionality and accessibility.
Preserving, waterproofing and decorating buildings.
Many resources for visitors aswell as new features for members.
Using technology to empower communities
The Community data platform; capturing the DNA of a place and fostering participation, for better design.
Heat pump and wind turbine sound calculations for PDRs
MCS publish updated sound calculation standards for permitted development installations.
Homes England creates largest housing-led site in the North
Successful, 34 hectare land acquisition with the residential allocation now completed.
Scottish apprenticeship training proposals
General support although better accountability and transparency is sought.
The history of building regulations
A story of belated action in response to crisis.
Moisture, fire safety and emerging trends in living walls
How wet is your wall?
Current policy explained and newly published consultation by the UK and Welsh Governments.
British architecture 1919–39. Book review.
Conservation of listed prefabs in Moseley.
Energy industry calls for urgent reform.
Heritage staff wellbeing at work survey.

























Comments
[edit] To make a comment about this article, click 'Add a comment' above. Separate your comments from any existing comments by inserting a horizontal line.