Baroque architecture
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Baroque architecture is a style that emerged in Italy in the late-16th century.
It was a more theatrical version of Renaissance architecture, with dramatic lighting and colour, illusory effects such as trompe l’oeil, and designs that played games with architectural features, sometimes leaving them incomplete.
Its buildings typically include central towers, domes, portico or other central projections in the main façade. As Baroque architecture coincided with European colonialism, it can be seen throughout much of the world; and in some regions, notably Germany and colonial South America, it lasted until the 18th century.
[edit] History
Baroque developed in the Counter-Reformation period, when the Catholic Church needed to reassert its waning influence across Europe in the face of the Protestant Reformation. One way of attracting new followers was to create overtly emotional and sensory displays in art and architecture. Church architecture appealed as much to the emotions as to the intellect of the faithful, attempting to persuade them into unconditional loyalty to the church. Approaching and entering a church became a symbolic, sensorial and mysterious experience.
While initially finding form in church and cathedral design, the style was later used as a visual demonstration of absolutist regimes in the form of elaborate royal palaces.
The late Baroque style is often referred to as Rococo or, in Spain and Spanish America, as Churrigueresque.
[edit] Style and characteristics
Baroque architecture is characterised by dynamic designs and complex architectural plan forms; intended to heighten feelings of motion and sensuality, and frequently based on the oval. There is often a mixture of the repetition, break-up and distortion of Renaissance classical motifs.
- Grandeur.
- Contrast.
- Curves and twists.
- Rich surface treatments.
- Gilded statuary.
- Bright colours.
- Vividly painted ceilings.
- Fragmented or deliberately incomplete elements.
- Large-scale frescoes.
- Dramatic central projections on an external façade.
- Use of plaster or stucco, marble or faux finishing.
- Illusory effects such as trompe l’oeil.
- Pear-shaped domes (more common in Eastern Europe baroque).
[edit] Notable buildings
The most notable practitioners of the baroque style in Italy included Gian Lorenzo Bernini, Carlo Maderno, and Francesco Borromini. Developing later, in central Europe the most notable architect was Johann Bernhard Fischer von Erlach. In Britain, baroque was adopted by Christopher Wren and Nicolas Hawksmoor.
Some of the most notable buildings incorporating the baroque style are:
- St. Paul’s Cathedral, London.
- Winter Palace, St. Petersburg.
- Karlskirche, Vienna.
- Palace of Versailles, Versailles.
- Les Invalides, Paris.
- St. Peter’s Square, Vatican City.
- San Carlo alle Quattro Fontane, Rome.
- St. John’s Co-Cathedral, Valletta, Malta.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Architectural styles.
- Art Deco.
- Bauhaus.
- Beaux Arts style.
- Belvedere.
- Classical architecture
- Eclecticism.
- Fountaine Hospital Almshouse.
- International Style.
- Italian Renaissance Revival style.
- Modernist architecture.
- Monopteros.
- Neoclassical architecture.
- Palladian architecture.
- Piazza.
- Postmodern architecture.
- Restoring Orleans House Octagon.
- Rococo.
- Scagliola.
- Stuart architecture.
- Trompe l’oeil.
- Zeitgeist.
Featured articles and news
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this...
National Apprenticeship Week 2026, 9-15 Feb
Shining a light on the positive impacts for businesses, their apprentices and the wider economy alike.
Applications and benefits of acoustic flooring
From commercial to retail.
From solid to sprung and ribbed to raised.
Strengthening industry collaboration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong Institute of Construction and The Chartered Institute of Building sign Memorandum of Understanding.
A detailed description from the experts at Cornish Lime.
IHBC planning for growth with corporate plan development
Grow with the Institute by volunteering and CP25 consultation.
Connecting ambition and action for designers and specifiers.
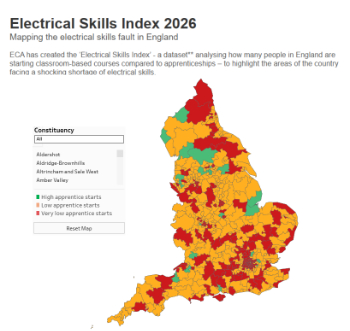
Electrical skills gap deepens as apprenticeship starts fall despite surging demand says ECA.
Built environment bodies deepen joint action on EDI
B.E.Inclusive initiative agree next phase of joint equity, diversity and inclusion (EDI) action plan.
Recognising culture as key to sustainable economic growth
Creative UK Provocation paper: Culture as Growth Infrastructure.
Futurebuild and UK Construction Week London Unite
Creating the UK’s Built Environment Super Event and over 25 other key partnerships.
Welsh and Scottish 2026 elections
Manifestos for the built environment for upcoming same May day elections.
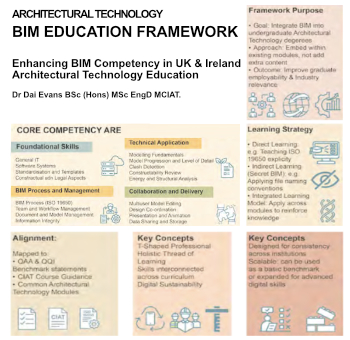
Advancing BIM education with a competency framework
“We don’t need people who can just draw in 3D. We need people who can think in data.”