BFRC window rating scheme WER
BFRC stands for the British Fenestration Rating Council. It is a wholly-owned subsidiary of the glazing industry’s trade association, the Glass and Glazing Federation.
The BFRC scheme is an Window Energy Rating (WER) scheme. It is based on a traffic-light style A-G ratings system for energy efficiency similar to that used for fridges, washing machines, cookers and so on. An A rating indicates a good level of energy efficiency, whilst G is the lowest possible rating.
Rated windows are provided with labels that include information about:
- The rating level of the window, from A-G.
- The energy loss rating in kilowatt hours per square metre per year.
- A U-value, indicating the thermal conductivity of the window.
- The effective heat loss due to air infiltration in W/m²K.
- Solar heat gain as a ratio of incident to transmitted solar radiation.
Windows rated A to C also carry the Energy Saving Recommended logo issued by the Energy Saving Trust. There is also now an A+ rating for the very highest performing windows.
The label gives an overall indication of how energy efficient the window is, how much air it will allow to penetrate into a building, the likelihood of condensation and the level of acoustic insulation and so on. It can also be used to demonstrate building regulations compliance for replacement windows.
The efficiency of windows is improved by double glazing, treble glazing, low-e coatings, the construction of the frame, the type of glass, the gas used to fill the sealed unit and so on. Generally, more efficient windows are more expensive, but the capital cost may be recovered during the life of the window life through lower energy bills. In addition, the conditions within the enclosed space are likely to be more comfortable.
BFRC claim that changing the windows on an average house from single glazing to energy efficient windows can save 18% in energy use (ref BFRC FAQ’s).
In September 2011, BFRC launched a Door Energy Ratings Scheme (DER).
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Domestic windows.
- Door energy rating.
- Double glazing.
- Double glazing v triple glazing.
- Emissivity.
- Energy certificates.
- g-value.
- Glass manifestation.
- Low-e glass.
- Pelmet.
- Secondary glazing.
- Shading coefficient.
- Solar heat gain coefficient.
- Sustainability.
- Thermal bridge.
- Triple glazing.
- Types of window.
- U value.
- Window parts.
[edit] External references
- BFRC.
Featured articles and news
Great British Energy install solar on school and NHS sites
200 schools and 200 NHS sites to get solar systems, as first project of the newly formed government initiative.
600 million for 60,000 more skilled construction workers
Announced by Treasury ahead of the Spring Statement.
The restoration of the novelist’s birthplace in Eastwood.
Life Critical Fire Safety External Wall System LCFS EWS
Breaking down what is meant by this now often used term.
PAC report on the Remediation of Dangerous Cladding
Recommendations on workforce, transparency, support, insurance, funding, fraud and mismanagement.
New towns, expanded settlements and housing delivery
Modular inquiry asks if new towns and expanded settlements are an effective means of delivering housing.
Building Engineering Business Survey Q1 2025
Survey shows growth remains flat as skill shortages and volatile pricing persist.
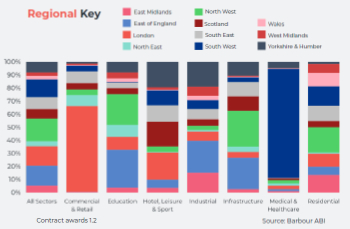
Construction contract awards remain buoyant
Infrastructure up but residential struggles.
Home builders call for suspension of Building Safety Levy
HBF with over 100 home builders write to the Chancellor.
CIOB Apprentice of the Year 2024/2025
CIOB names James Monk a quantity surveyor from Cambridge as the winner.
Warm Homes Plan and existing energy bill support policies
Breaking down what existing policies are and what they do.
Treasury responds to sector submission on Warm Homes
Trade associations call on Government to make good on manifesto pledge for the upgrading of 5 million homes.
A tour through Robotic Installation Systems for Elevators, Innovation Labs, MetaCore and PORT tech.
A dynamic brand built for impact stitched into BSRIA’s building fabric.
BS 9991:2024 and the recently published CLC advisory note
Fire safety in the design, management and use of residential buildings. Code of practice.