Laminated glass
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Laminated glass (sometimes called toughened laminated glass) comprises two or more layers of glass sandwiched together with tear-resistant plastic film interlayers (usually polyvinyl butyral (PVB) or ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA). The aim is to create a glass composite which can absorb the energy of a person or object that strikes it, preventing penetration of the pane and potential injuries that might result from flying fragments of broken glass.
An additional benefit of laminated glass is that most ultraviolet radiation can be blocked by the PVB or EVA interlayer. Thermoset EVA layers can block up to 99.9% of UV rays.
[edit] Applications
Laminated glass can be used for safety or security reasons. It is used for architectural applications where for example, the glass could fall from a height and shatter, and also for roof, balcony and terrace balustrading, as well as for skylights. It can also be used as a decorative material due to the wide variety of interlayers available, e.g coloured, textured, meshed or patterned. It is particularly useful for windows and shopfronts in areas prone to hurricanes.
In addition to flat sheets, it can be supplied in curved sections, as may be required for car windscreens.
[edit] Manufacture
Bonding together the alternating layers of, typically annealed glass, and plastic film is usually achieved through the use of heat and pressure created by an autoclave.
Manufacture can involve using heat-strengthened glass, which, when it breaks, does so into large pieces held in the frame by the PVB inter-layer. Or it can be made from tempered glass, where the sheet may fall out of the frame but will mostly stay together due to the interlayer.
Digital printing for special effects can be created by printing on to the glass prior to laminating or printing onto the interlayer.
[edit] Configurations
Laminated glass is available in various thicknesses and configurations. A typical glass-layers configuration can comprise 2.5mm glass – 0.38mm interlayer – 2.5mm glass, resulting in ‘5.38 laminated glass’.
Thicker glass and multiple laminates giver a stronger product. Thicker configurations such as double– or triple-laminate with interlayers (int) can include the following:
[edit] Double laminate:
- 6mm - int - 6mm.
- 8mm - int - 8mm.
- 10mm - int - 10mm.
[edit] Triple laminate:
- 6mm - int - 6mm - int -6mm.
- 8mm - int - 8mm - int -8mm.
- 10mm - int - 10mm - int -10mm.
The cockpit of an aircraft such as a Boeing 747 may include a triple-laminated glass construction comprising three layers of 4mm toughened glass with 2.6mm PVB layers in between, making a total glass thickness of 17.2mm.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- BFRC window rating scheme.
- BREEAM Visual comfort View out.
- Curved glass.
- Daylit space.
- Domestic windows.
- Double glazing.
- Emissivity.
- Float glass process.
- Glass.
- Low-E glass.
- Overheating.
- Patent glazing.
- Preventing overheating.
- R-value.
- Rights to light.
- Safety glass.
- Secondary glazing.
- Security glazing.
- Structural glass assembly.
- Suction lifter.
- Types of window.
- U-value.
- Window.
Featured articles and news
Restoring Alexander Pope's grotto
The only surviving part of his villa in Twickenham.
International Women's Day 8 March, 2025
Accelerating Action for For ALL Women and Girls: Rights. Equality. Empowerment.
Lack of construction careers advice threatens housing targets
CIOB warning on Government plans to accelerate housebuilding and development.
Shelter from the storm in Ukraine
Ukraine’s architects paving the path to recovery.
BSRIA market intelligence division key appointment
Lisa Wiltshire to lead rapidly growing Market Intelligence division.
A blueprint for construction’s sustainability efforts
Practical steps to achieve the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
Timber in Construction Roadmap
Ambitious plans from the Government to increase the use of timber in construction.
ECA digital series unveils road to net-zero.
Retrofit and Decarbonisation framework N9 launched
Aligned with LHCPG social value strategy and the Gold Standard.
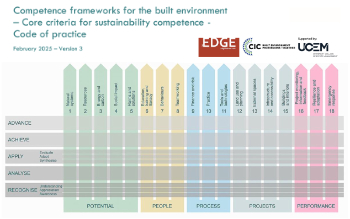
Competence framework for sustainability
In the built environment launched by CIC and the Edge.
Institute of Roofing members welcomed into CIOB
IoR members transition to CIOB membership based on individual expertise and qualifications.
Join the Building Safety Linkedin group to stay up-to-date and join the debate.
Government responds to the final Grenfell Inquiry report
A with a brief summary with reactions to their response.
A brief description and background to this new February law.
Everything you need to know about building conservation and the historic environment.