Smart lighting
Contents |
[edit] What is smart lighting?
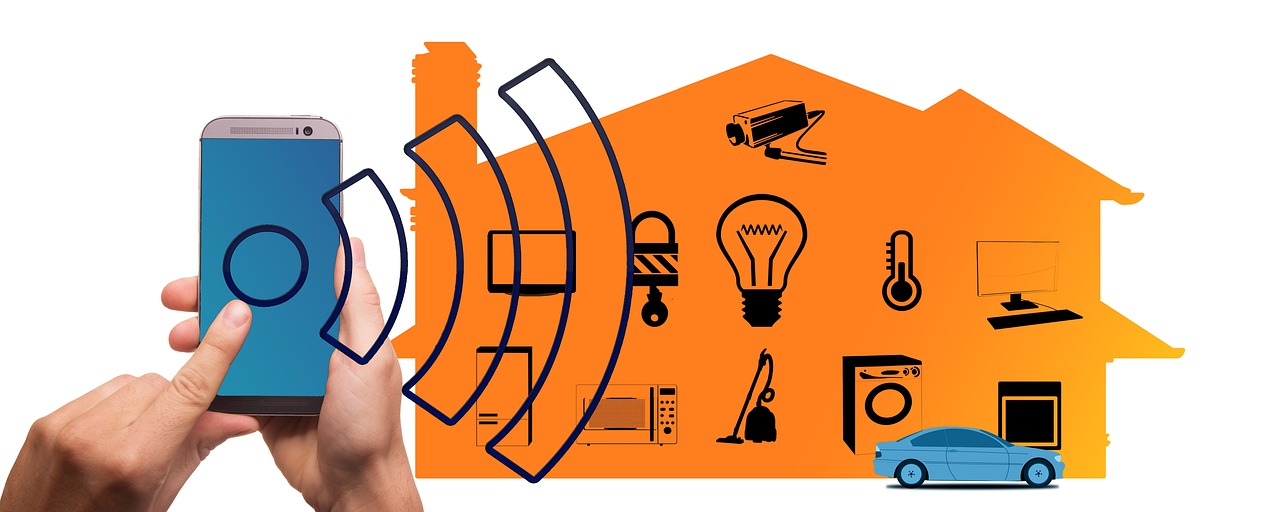
Smart lighting allows users to control and customise the lighting in a building using remote devices such as smartphones or tablets. It is designed to be convenient, energy-efficient, and programmable, and can be used to create a variety of lighting environments for different tasks or occasions.
[edit] What are the advantages of smart lighting?
One of the main advantages of smart lighting its ability to control lighting remotely. This can be done using a smartphone or tablet, or through a smart home hub. With smart lighting, users can turn lights on or off, dim them, or change their colour from anywhere with an internet connection. This can be particularly useful when the user is away from the building, as it allows them to turn the lights off if they forgot to do so before leaving, or to turn them on when they are on their way home.
Smart lighting is also energy-efficient. Many smart bulbs use LED technology to reduce energy consumption. Additionally, the ability to control lighting remotely means that users can turn off lights that are not needed.
Many smart bulbs can be programmed to change colour, allowing users to create a variety of different lighting environments for different tasks or occasions. For example, a user might choose a softer, warmer light for relaxation or a cooler, brighter light for tasks such as reading or cooking.
Smart lighting can be integrated with other smart devices, such as thermostats and security systems, allowing control all of a property's systems from one central location.
Smart lighting can also be programmed to turn on and off at certain times, creating the illusion that someone is home even when they are not. This can deter burglars and increase overall safety and security.
[edit] What are the disadvantages of smart lighting?
Smart lighting systems can be expensive to instal, especially if you want to retrofit your entire home with smart bulbs. The cost of smart bulbs can also be higher than traditional bulbs. They can also be complex to set up and use, especially for people who are not tech-savvy. It may take some time to learn how to use all of the features and functions of a smart lighting system.
Most smart lighting systems require a central hub to function. If this hub fails or loses power, the smart lighting system may not work properly. Smart lighting systems also require an internet connection to function properly. If the internet goes down, the smart lighting system may not work properly.
Smart lighting systems may not be compatible with older homes or buildings that do not have the necessary wiring or infrastructure in place.
Some people may also be concerned about the privacy implications of having a smart lighting system that can be controlled remotely.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Commercial lighting.
- General lighting v task lighting.
- Light fitting.
- Lighting and energy efficiency.
- Lighting control.
- Lighting for circadian rhythms.
- Lighting in commercial buildings.
- Lighting of construction sites.
- Lighting.
- Natural light.
- Smart lighting market to 2020.
- Smart office lighting.
- Types of lamp.
- Types of lighting.
[edit] External references
- "Smart lighting explained: What it is and why you should care." CNET. https://www.cnet.com/news/smart-lighting-explained-what-it-is-and-why-you-should-care/
- "Smart lighting: A beginner's guide." Techradar. https://www.techradar.com/uk/news/smart-lighting-a-beginners-guide
- "Smart Lighting: The Benefits and Drawbacks." Electronic House. https://www.electronichouse.com/smart-home/smart-lighting-the-benefits-and-drawbacks/
Featured articles and news
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.






















Comments
[edit] To make a comment about this article, or to suggest changes, click 'Add a comment' above. Separate your comments from any existing comments by inserting a horizontal line.