Sound insulation in buildings
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Sound insulation describes the reduction in sound across a partition. The sound insulation across a good conventional, lightweight, office to office construction is typically in the order of 45 dB Dw.
This means that if the sound level in the source room is around 65 dB (a typical level for speech), the sound level in the adjacent room, the receiver room, will be approximately 20 dB (barely audible).
If sound levels are increased in the source room to 75 dB (raised voice), sound levels within the adjacent room will also increase to around 30 dB (audible). Sound insulation therefore describes the level of sound lost across a partition and not the level of sound within a adjacent room.
[edit] Privacy
Privacy describes the perceived sound reduction across a wall. Privacy is a function of both sound insulation and background noise. Background noise is made up of services noise and environmental noise sources breaking in through the facade or open windows, vents etc.
If the background noise within a room is increased by 5 to 10 dB, the perceived level of privacy across a partition is also increased by 5 to 10 dB. Therefore, when looking at required sound insulation levels on-site, it is important to consider both the background noise in the receiver room and the sound insulation across the partition.
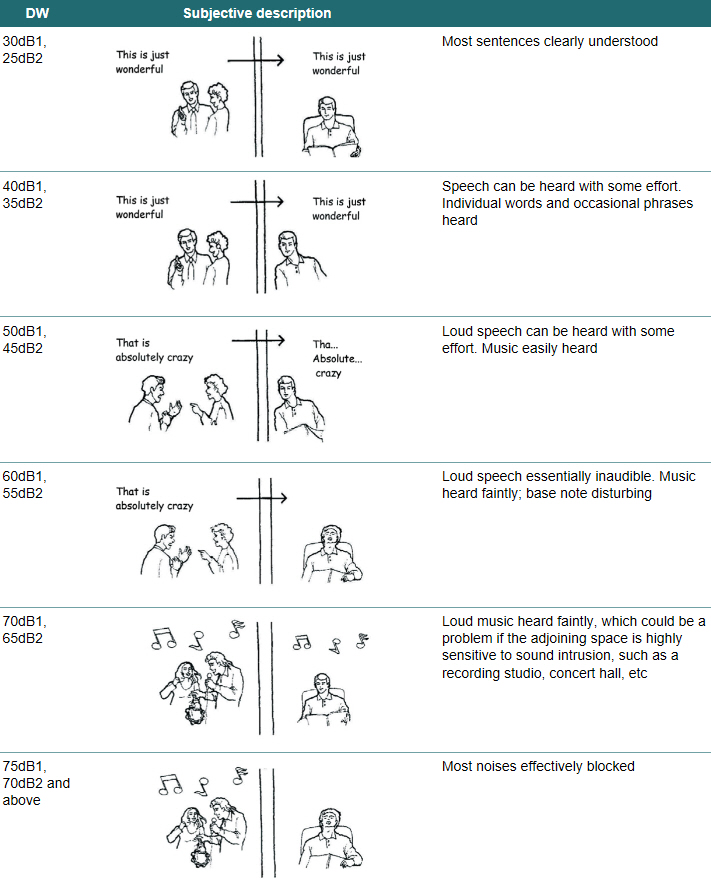
[edit] Subjective description of sound insulation
The table below provides an illustrative representation of privacy. This table specifies two Dw levels for a partition, one for background noise levels in the receiver room of 35 dBA1, and the second for background noise levels of 40 dBA2.
[edit] Rw (Lab Tested Sound Reduction Index) and Dw (On Site Sound Reduction Index)
Two parameters are used to describe the sound insulation of a partition, Dw and Rw. Dw represents the sound insulation between rooms on-site. Since these figures describe the final site requirements, Dw levels are specified by clients and Building Regulations. Rw represents the lab tested sound insulation of an element making up a partition wall/floor type. Due to flanking and other factors, lab rated sound reduction levels will not be achieved on-site.
Conventionally, there is a 5 - 10 dB reduction between a Rw lab tested figure and an on-site Dw figure. The conversion between Dw and Rw is relatively complex and takes into consideration receiver room volume, receiver room reverberation times and the area of the separating partition. The conversion between Rw and Dw should always be calculated.
NB: Approved document E, Resistance to the passage of sound, defines the sound reduction index (which it describes as 'R') as a '...quantity, measured in a laboratory, which characterises the sound insulating properties of a material or building element in a stated frequency band. See BS EN ISO 140-3:1995.'
This article was created by --MACH Acoustics 13:06, 28 November 2013 (UTC)
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Acoustic insulation market.
- Acoustic design for health and wellbeing.
- Acoustic louvre.
- Acoustics in the workplace.
- Airborne sound.
- Approved Document E.
- Ash deafening.
- BREEAM Insulation.
- Building acoustics.
- Building Bulletin 93: acoustic design of schools.
- Decibel.
- Flanking sound.
- Impact sound.
- Mineral wool.
- Movable walls.
- Noise - doors and windows.
- Noise nuisance.
- Part E compliance.
- Pre-completion sound testing.
- Reverberation.
- Robust details certification scheme.
- Room acoustics.
- Rw and Dw/DnTw in Acoustics
- Sound absorption.
- Sound absorption coefficient.
- Sound frequency.
- Sound insulation in dwellings: Part 1: An introduction (GG 83-1).
- Sound insulation in dwellings: Part 3: Material change of use (conversions) (GG 83-3).
- Sound insulation testing.
- Sound v noise.
- Sound reduction index (SRI).
- Structure-borne sound.
- Suitable insulation can help preserve the golden sound of silence.
[edit] External references
- MACH Acoustics: Subjective Evaluation and Conversion between RW and DW.
- ParkerJones Acoustics: Rw and DnT,w – What do they mean?
Featured articles and news
From studies, to books to a new project, with founder Emma Walshaw.
Types of drawings for building design
Still one of the most popular articles the A-Z of drawings.
Who, or What Does the Building Safety Act Apply To?
From compliance to competence in brief.
The remarkable story of a Highland architect.
Commissioning Responsibilities Framework BG 88/2025
BSRIA guidance on establishing clear roles and responsibilities for commissioning tasks.
An architectural movement to love or hate.
Don’t take British stone for granted
It won’t survive on supplying the heritage sector alone.
The Constructing Excellence Value Toolkit
Driving value-based decision making in construction.
Meet CIOB event in Northern Ireland
Inspiring the next generation of construction talent.
Reasons for using MVHR systems
6 reasons for a whole-house approach to ventilation.
Supplementary Planning Documents, a reminder
As used by the City of London to introduce a Retrofit first policy.
The what, how, why and when of deposit return schemes
Circular economy steps for plastic bottles and cans in England and Northern Ireland draws.
Join forces and share Building Safety knowledge in 2025
Why and how to contribute to the Building Safety Wiki.
Reporting on Payment Practices and Performance Regs
Approved amendment coming into effect 1 March 2025.
A new CIOB TIS on discharging CDM 2015 duties
Practical steps that can be undertaken in the Management of Contractors to discharge the relevant CDM 2015 duties.
Planning for homes by transport hubs
Next steps for infrastructure following the updated NPPF.
























Comments
Interested in learning about acoustics and building construction techniques for sound attenuation with a focus on the use of resilient sound isolation clips, check out the following link: http://aecdai.ly/9m