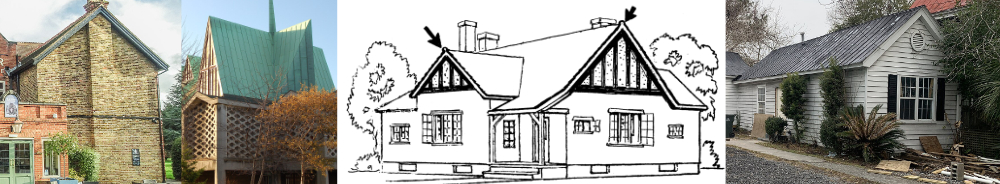
Gable roof
A gable roof, might be considered one of the most standard kinds of roof, where two halves of the roof meet at the highest point in a centre line, pitching down to an overhang on the side walls. The stright sides are closed up to the pitch by the gable, gable walls or gable ends which form an upper triangle enclosing the roof space.
Traditionally gable roofs were often cold timber roofs with the rafters laid at an angle, cut in at the top with bird mouth notches to sit on the ridge beam at the highest point, and tied together at the bottom with perpendicular tie beams. All parts working together structurally to form trusses, with the space above the tie beams being the vented cold roof space, usually vented at the eaves (where the joint of the rafters and tie beams sit on the supporting walls) and the space below being the warm insulated space, often with insultation between and above the tie beams. Other additions to the trusses to increase strength of efficiency might include king posts, queen posts and purlins, forming different types of trusses, roof formed of trusses that include purlins might also be called purlin rooves.
Other specific descriptions of a gable roof might include front gable, side gable and cross gable. A side or front gable simple describes where the gable end is in relation to the street, at the front or entrance to the house or at the side, with the pitch roof coming to the front. A cross gable roof is where two or more building blocks, with roof gable meet perpendicular to one another, thus creating a valley roof at the point where the two pitches meet and run into a valley gutter.
There are also other varieties of what might be called a gable roof, such as the Dutch gable and the box gable. The dutch gable being a hybrid between a hip roof and a gable roof, where the primarily hip roof has a gable roof at its uppermost point. The box gable is a standard gable, with the difference being at the gable ends, where the gable at the roof height protrudes from the wall below the gable end, so the gable ends overhang the wall as such.
For other related articles see types of roof, domestic roofs and types of truss.
See also: Gable and inverted gable.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
Homes England creates largest housing-led site in the North
Successful, 34 hectare land acquisition with the residential allocation now completed.
Scottish apprenticeship training proposals
General support although better accountability and transparency is sought.
The history of building regulations
A story of belated action in response to crisis.
Moisture, fire safety and emerging trends in living walls
How wet is your wall?
Current policy explained and newly published consultation by the UK and Welsh Governments.
British architecture 1919–39. Book review.
Conservation of listed prefabs in Moseley.
Energy industry calls for urgent reform.
Heritage staff wellbeing at work survey.
A five minute introduction.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Showcasing the very best electrotechnical and engineering services for half a century.
Welsh government consults on HRBs and reg changes
Seeking feedback on a new regulatory regime and a broad range of issues.
CIOB Client Guide (2nd edition) March 2025
Free download covering statutory dutyholder roles under the Building Safety Act and much more.
Minister quizzed, as responsibility transfers to MHCLG and BSR publishes new building control guidance.
UK environmental regulations reform 2025
Amid wider new approaches to ensure regulators and regulation support growth.
BSRIA Statutory Compliance Inspection Checklist
BG80/2025 now significantly updated to include requirements related to important changes in legislation.