Folly

|
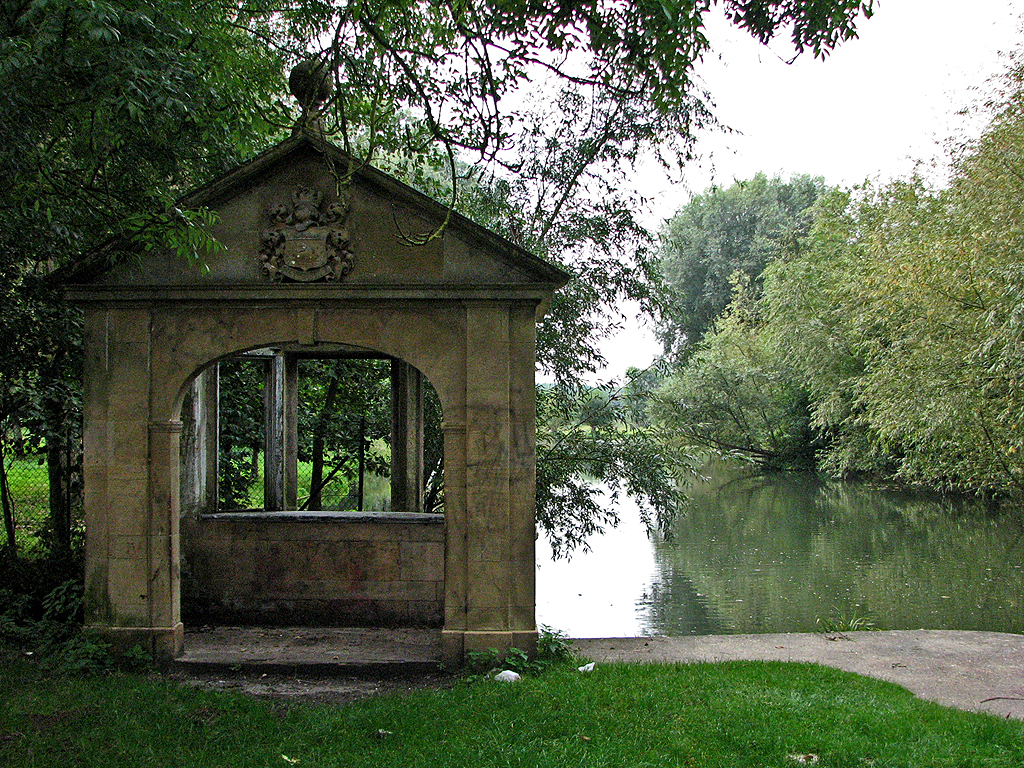
| Hodson’s Folly was built in 1887 by John Hodson so that he could keep a watchful eye on his daughters bathing in the river while overseeing his nearby fish hatchery. The land used was common land which Hodson, who was at one point a butler’s assistant at Pembroke College, had annexed without permission. As a speculative builder, Hodson excelled: his building sports a coat of arms, showing a swan in a rain storm, and the summer house and its garden are in many ways a Cambridge college in miniature. (From the University of Cambridge website.) |
In architecture, a folly is typically a costly building that has been constructed for no specific purpose, or for which the original purpose has become obsolete or obscured over time. Its primary function is decorative, although it is sometimes also meant to demonstrate wealth or symbolise virtues.
In some instances, the construction of follies served as a method of employment for those who sought work. They also created projects for artisans who may have been struggling during difficult times.
Follies were often whimsical or eccentric structures that were made to project a false sense of age. For instance, they were made to look like ancient ruins (or sham ruins) despite being relatively modern constructions.
They were frequently constructed as towers, and like eyecatchers, they serve to create a focal point in a landscape, often on the grounds of a stately home. This attracts visual attention or otherwise punctuates the vista with a sense of drama.
Authentic ruins found on estates served as the original model for follies, which were first introduced in the 17th century. They became increasingly popular through the 18th and 19th centuries, adopting more exotic locations and depicting more fanciful eras.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.