Entasis
Entasis in architecture can be seen mainly in the design of classical columns to correct what would be an optical illusion. But is also seen in the construction of spires and other upright members.
Typically viewed from below, a column with straight parallel sides that taper toward the top can appear to be concave in outline. Classical designers therefore created a slight convexity (swelling) in the middle length of the column to correct the appearance of concavity. It is thought that the application of entasis also created a greater illusion of strength and height.
The word entasis derives from the Greek word ‘εντενω’ (enteino – to stretch or make taut) and the term is believed to have been first used by the Roman military architect Vitruvius (c.80-15BC).
Entasis maybe seen in classical architecture all over the world, such as on the Doric columns of the Parthenon, where it is said there is not a single straight vertical line in the surrounding colonnade (peristyle). With each vertical bowed, the projected lines are thought to meet at a point in space 3.5km away. The Renaissance architect Andrea Palladio also employed entasis and this can be seen on many of his works, such as the Villa Capra (La Rotunda), just outside Vicenza, northern Italy, built 1567-1570.
[edit] Speculation
There has been much conjecture over the use of entasis in architecture because there is no evidence to fully explain why the early classical builders used the technique. Some have argued that entasis makes a column appear to bulge and therefore is expressing the notion of strength as it takes the weight of whatever is above it. This may explain the exaggerated entasis applied to the columns of the First Hera temple at Paestum, Italy, that appear to bulge significantly at their lower extremities.
Others say that there is a sound engineering explanation for applying the technique, as a column that bulges in its middle section is stronger than a column whose diameter changes in a progressive, linear way.
[edit] Other applications
Entasis has been used in construction before and after the period of classical antiquity: it is thought that the builders of the pyramids may have been the first to use it and it has been employed on constructions elsewhere ever since.
The Inca employed entasis in their walls and doorways and it can also be seen in the monasteries and fortress architecture of Tibet and Bhutan. Building a battered (sloping) wall simply straight can make it appear to bulge outwards. Another example is the spire of the 14th century steeple of All Hallows parish church in Gedling, Northamptonshire.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
ECA support for Gate Safe’s Safe School Gates Campaign.
Core construction skills explained
Preparing for a career in construction.
Retrofitting for resilience with the Leicester Resilience Hub
Community-serving facilities, enhanced as support and essential services for climate-related disruptions.
Some of the articles relating to water, here to browse. Any missing?
Recognisable Gothic characters, designed to dramatically spout water away from buildings.
A case study and a warning to would-be developers
Creating four dwellings... after half a century of doing this job, why, oh why, is it so difficult?
Reform of the fire engineering profession
Fire Engineers Advisory Panel: Authoritative Statement, reactions and next steps.
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this...
National Apprenticeship Week 2026, 9-15 Feb
Shining a light on the positive impacts for businesses, their apprentices and the wider economy alike.
Applications and benefits of acoustic flooring
From commercial to retail.
From solid to sprung and ribbed to raised.
Strengthening industry collaboration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong Institute of Construction and The Chartered Institute of Building sign Memorandum of Understanding.
A detailed description from the experts at Cornish Lime.
IHBC planning for growth with corporate plan development
Grow with the Institute by volunteering and CP25 consultation.
Connecting ambition and action for designers and specifiers.
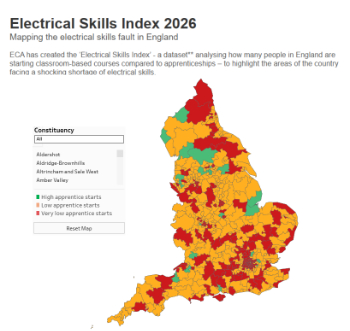
Electrical skills gap deepens as apprenticeship starts fall despite surging demand says ECA.
Built environment bodies deepen joint action on EDI
B.E.Inclusive initiative agree next phase of joint equity, diversity and inclusion (EDI) action plan.
Recognising culture as key to sustainable economic growth
Creative UK Provocation paper: Culture as Growth Infrastructure.