Bascule bridge

|
| London's illuminated Tower Bridge opening its bascule portion as PS Waverley approaches to pass underneath. |
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Bridges are a common feature of the built environment and one of the key elements of civil engineering. The basic principles of bridge design are dependent on the load-bearing structure. These are generally beam, arch or suspension structures.
Some bridges are also defined by other characteristics, for example a movable bridge is defined by its functionality. These bridges are designed in a way that allows them to accommodate different situations and different types of traffic. One kind of movable bridge is a bascule bridge or lifting bridge.
[edit] Bascule bridges
This type of bridge can be raised in order to provide clearance for waterway traffic. Bascule bridges are generally considered to be structurally reliable and economical (both in terms of construction and operation).
The term bascule comes from the French word associated with balancing mechanical devices. In the United States and other parts of the world, a bascule bridge may be referred to as a drawbridge or draw bridge. In Great Britain, the term drawbridge is more commonly associated with castle entrances.
[edit] Operations
Bascule bridges are supported on an axis perpendicular to their longitudinal centerline. They lift along their centre of gravity. This creates a balance for the lifted span(s) on both sides of the horizontal pivotal axis.
The balance of weight may be intentionally adjusted to accommodate frequent activity. For instance, if the bridge needs to be opened for frequent waterway traffic, its weight distribution will be designed for this purpose. This is referred to as counterweight heavy. If the tendency is to keep the bridge closed, then the weight distribution will be designed for this purpose. This is referred to as heavy span.
[edit] Platforms
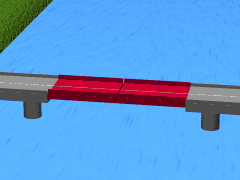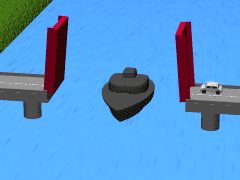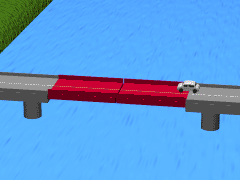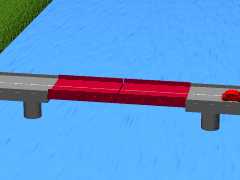
Bascule bridges tend to have one platform spanning from an area or two that are joined in the middle. The platforms are sometimes referred to as a leafs or spans. Bridges with one platform are called single-leaf; those with two are called double-leaf. In rare instances, there are also triple- and quadruple-leaf structures.
|
This animation depicts a double-leaf bascule bridge in operation. |
These platforms are often controlled by a counterweight that balances them. Counterweights require very little energy to operate. This means that the bridge can be opened quickly for water traffic to pass underneath.
There are three main types of rolling bascule bridges that use counterweights. In these instances the counterweights may be located above or below the bridge deck.
- Fixed trunnion (or Chicago).
- Rolling lift trunnion (or Scherzer).
- Rall type (a hybrid construction that combines a rolling lift counterweight approach with other methods of operation).
There are also rolling bascule bridges that do not use counterweights. Instead, they are lifted by a gear that rolls along a horizontal rack.
[edit] Origins of bascule bridges
There is evidence that bascule bridges were used in ancient times. In the Middle Ages, they were used for defensive purposes in Europe. These drawbridges were typically operated by counterweights and winches.
In 1176, Peter Colechurch began work on the original version of London Bridge (commonly referred to as Old London Bridge). This stone structure included a wooden drawbridge which was operational until the late 1400s. When Old London Bridge was replaced in 1831, the new structure did not include a drawbridge (nor did its subsequent replacement, which opened in 1972).
By the time of the Industrial Revolution, the adoption of modern technologies and the introduction of new power sources made it possible to create large spans. When the double-leaf Tower Bridge was built in the late 1800s, it incorporated both bascule and suspension bridge elements that could accommodate multiple types of traffic.
[edit] Noteworthy bascule bridges
Built in 1913, the world’s longest double-leaf bascule bridge is the Broadway Bridge in Portland, Oregon. Employing the Rall type of construction, the Broadway Bridge was added to the US National Register of Historic Places in November 2012.
 Broadway Bridge in Portland, Oregon (USA). Broadway Bridge in Portland, Oregon (USA).
|
In addition to Tower Bridge, other bascule bridges in the UK include:
1923 - White Cart Bridge, Renfrew. This Scherzer rolling lift bascule bridge is still capable of opening, which allows the Doosan Babcock factory to move large loads on the river.
1924 - The Bann Bridge, Coleraine. This is the only railway bascule bridge in Northern Ireland. The bridge serves the Belfast – Londonderry railway across the River Bann.
|
Bann Bridge, Coleraine (Northern Ireland). |
1925 - Corporation Bridge, Grimsby. This electrically powered Scherzer rolling lift bascule bridge was built to replace an earlier swing bridge dating from 1872. It is a Grade II Listed structure.
1932 - Bascule Bridge, Stanley Dock, Liverpool. The Grade II Listed bascule bridge in Liverpool's docklands is only one of a handful of its type in the UK.
|
Bascule Bridge, Stanley Dock, Liverpool (England). |
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
The history of building regulations
A story of belated action in response to crisis.
Moisture, fire safety and emerging trends in living walls
How wet is your wall?
Current policy explained and newly published consultation by the UK and Welsh Governments.
British architecture 1919–39. Book review.
Conservation of listed prefabs in Moseley.
Energy industry calls for urgent reform.
Heritage staff wellbeing at work survey.
A five minute introduction.
50th Golden anniversary ECA Edmundson apprentice award
Showcasing the very best electrotechnical and engineering services for half a century.
Welsh government consults on HRBs and reg changes
Seeking feedback on a new regulatory regime and a broad range of issues.
CIOB Client Guide (2nd edition) March 2025
Free download covering statutory dutyholder roles under the Building Safety Act and much more.
AI and automation in 3D modelling and spatial design
Can almost half of design development tasks be automated?
Minister quizzed, as responsibility transfers to MHCLG and BSR publishes new building control guidance.
UK environmental regulations reform 2025
Amid wider new approaches to ensure regulators and regulation support growth.
The maintenance challenge of tenements.
BSRIA Statutory Compliance Inspection Checklist
BG80/2025 now significantly updated to include requirements related to important changes in legislation.