Weathering steel
Weathering steel (also known by the trademark COR-TEN steel) is a form of high-strength, low alloy steel originally developed in the 1930's by United States Steel. It is a steel alloy, chemically composed to form a stable rust-like appearance that can resist corrosion and abrasion, by forming a protective surface layer, or patina.
The protective layer’s increased resistance is produced by the alloying elements and their particular distribution and concentration. When subjected to the influence of the weather, the protective surface layer continuously develops and regenerates, allowing the rust to form.
Weathering steel is often used in external sculptures, the most iconic of which is the Angel of the North in Gateshead. It can be used in bridges and other large structural applications, such as the New River Gorge Bridge, and it is becoming an increasingly popular design choice for buildings, often used alongside materials such as glass and terracotta. An example of such a building is the distinctive Broadcasting Tower in Leeds (see top image).
The advantages of weathering steel are that because it is already weathered and ‘rusted’, there are very low maintenance costs, it can be installed easily, and the need for a protective paint system is removed. Studies have found that bridges fabricated from unpainted weathering steel can achieve a design life of 120 years with only nominal maintenance, due to the low corrosion rate.
However, there are several challenges to weathering steel. It is unsuitable for use in marine or coastal environments, and in humid subtropical climates the patina may continue to corrode instead of stabilising into a protective layer. In addition, interface details require careful design as run-off water from wet rusted steel may negatively impact on other materials, such as staining glass. This is a particular problem in the first years after installation.
Special welding techniques or materials may be needed to ensure that weld-points weather at the same rate as the other materials.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this...
National Apprenticeship Week 2026, 9-15 Feb
Shining a light on the positive impacts for businesses, their apprentices and the wider economy alike.
Applications and benefits of acoustic flooring
From commercial to retail.
From solid to sprung and ribbed to raised.
Strengthening industry collaboration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong Institute of Construction and The Chartered Institute of Building sign Memorandum of Understanding.
A detailed description from the experts at Cornish Lime.
IHBC planning for growth with corporate plan development
Grow with the Institute by volunteering and CP25 consultation.
Connecting ambition and action for designers and specifiers.
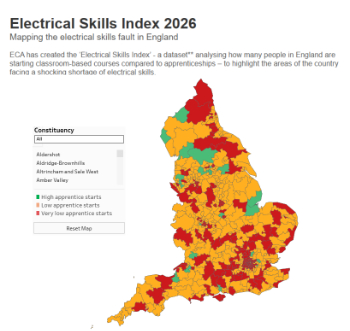
Electrical skills gap deepens as apprenticeship starts fall despite surging demand says ECA.
Built environment bodies deepen joint action on EDI
B.E.Inclusive initiative agree next phase of joint equity, diversity and inclusion (EDI) action plan.
Recognising culture as key to sustainable economic growth
Creative UK Provocation paper: Culture as Growth Infrastructure.
Futurebuild and UK Construction Week London Unite
Creating the UK’s Built Environment Super Event and over 25 other key partnerships.
Welsh and Scottish 2026 elections
Manifestos for the built environment for upcoming same May day elections.
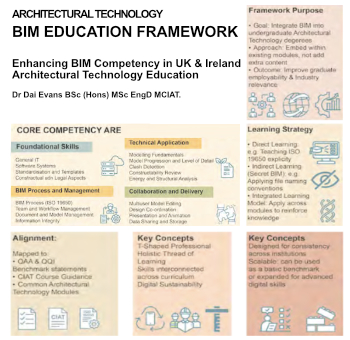
Advancing BIM education with a competency framework
“We don’t need people who can just draw in 3D. We need people who can think in data.”