Safety signs
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
The requirement for safety signs was mandated by the Health and safety at work etc act 1974. This was further enforced by the Health and Safety (Safety Signs and Signals) Regulations 1996.
The regulations require that safety signs are provided and maintained in circumstances where a health and safety risk is present that other methods have not been employed to remove or control. The primary aim of such signage is to further reduce risks presented by the hazards.
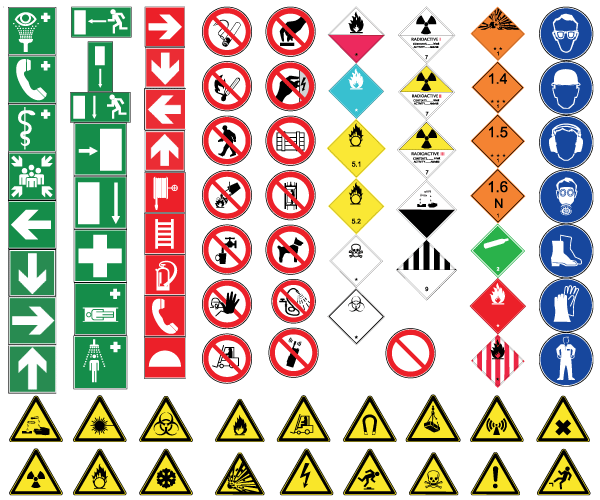
Signs convey information or instructions through a combination of shape, colour, and symbol (pictogram). Supplementary text can also be provided, such as ‘Fire exit’. Signs can be illuminated by using transparent or translucent materials lit from behind.
A number of different types of safety sign are described below.
[edit] Prohibition signs
Prohibition signs prohibit action which is likely to increase or cause danger, such as ‘No entry’. They are characterised by a round shape, and can either be a black pictogram on a white background, or can have red edging and a diagonal line.
[edit] Warning signs
Warning signs warn of a hazard or danger, such as ‘Danger: Toxic materials’. They are characterised by a triangular shape, and usually feature a black pictogram on a yellow background with black edging.
[edit] Mandatory signs
Mandatory signs prescribe specific behaviour, such as ‘Eye protection must be worn’. They are characterised by a round shape, and usually feature a white pictogram on a blue background.
[edit] Emergency escape or first-aid signs
Emergency escape and first-aid signs provide information on emergency exits, first aid or rescue facilities, such as ‘Emergency exit’. They are characterised by a rectangular or square shape, and usually feature a white pictogram on a green background.
They must be well maintained, and able to function during a power failure. The light from illuminated signs should be bright enough to be seen without causing glare.
[edit] Fire safety sign
A fire safety sign is defined as a sign which provides:
- Warning in case of fire.
- Information on escape routes and emergency exits (coloured green).
- Information on the identification or location of firefighting equipment (coloured red).
Fire exit signs should be displayed immediately above or near to the exit opening, where it is least likely to be obscured or obstructed by smoke. Buildings that have multiple occupants should adopt a common approach to the provision of fire safety signs, to avoid confusion about exit routes.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
Amendment to the GB Energy Bill welcomed by ECA
Move prevents nationally-owned energy company from investing in solar panels produced by modern slavery.
Gregor Harvie argues that AI is state-sanctioned theft of IP.
Heat pumps, vehicle chargers and heating appliances must be sold with smart functionality.
Experimental AI housing target help for councils
Experimental AI could help councils meet housing targets by digitising records.
New-style degrees set for reformed ARB accreditation
Following the ARB Tomorrow's Architects competency outcomes for Architects.
BSRIA Occupant Wellbeing survey BOW
Occupant satisfaction and wellbeing tool inc. physical environment, indoor facilities, functionality and accessibility.
Preserving, waterproofing and decorating buildings.
Many resources for visitors aswell as new features for members.
Using technology to empower communities
The Community data platform; capturing the DNA of a place and fostering participation, for better design.
Heat pump and wind turbine sound calculations for PDRs
MCS publish updated sound calculation standards for permitted development installations.
Homes England creates largest housing-led site in the North
Successful, 34 hectare land acquisition with the residential allocation now completed.
Scottish apprenticeship training proposals
General support although better accountability and transparency is sought.
The history of building regulations
A story of belated action in response to crisis.
Moisture, fire safety and emerging trends in living walls
How wet is your wall?
Current policy explained and newly published consultation by the UK and Welsh Governments.
British architecture 1919–39. Book review.
Conservation of listed prefabs in Moseley.
Energy industry calls for urgent reform.