Freezing method for stabilising soils
Freezing can be used as a method of stabilising water-saturated soils and preventing collapse next to excavations. By freezing the soil until it becomes impervious, it enables workers and plant to operate safely inside the ‘ice wall’ that is formed. In this way, deep earthworks can take place.
In order to produce the low temperatures, steel freeze pipes are installed at approximately 1 m centres around the site that is to be excavated. The pipes are comprised of two tubes. The outer tube is 100-150 mm in diameter, is sealed at the bottom and connected at the top to a return pipe. The inner tube is 38-75 mm in diameter, is open at the bottom and connected to the flow pipe at the top.
These pipes carry chilled brine which is pumped down the inner tube. A refrigeration plant is used to cool the liquid, constantly re-circulating it through the pipes. The brine temperature ranges from -15 to -25-degrees, although the freezing medium must have a freezing point that is well below this temperature range, meaning that a solution of calcium chloride or magnesium chloride is often used.
For the method to be employed there must be moisture content of 8% of the voids. Using a brine medium, the time to obtain a wall of ice depends on the spacing of the pipes, the refrigeration quantity and the type of soil. For example, with pipes spaced at 1 m centres, a frozen wall measuring 1 m thick in sand and gravel takes 10-12 days, and 15-17 days in clay. An observation borehole in the centre of the treated area is sunk to determine whether the frozen wall is completely continuous and excavation work can begin.
Where rapid freezing is required, liquid nitrogen is used as the freezing medium, and this can reduce the freezing time to a few days.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
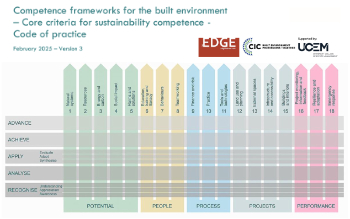
Competence framework for sustainability
In the built environment launched by CIC and the Edge.
Institute of Roofing members welcomed into CIOB
IoR members transition to CIOB membership based on individual expertise and qualifications.
Join the Building Safety Linkedin group to stay up-to-date and join the debate.
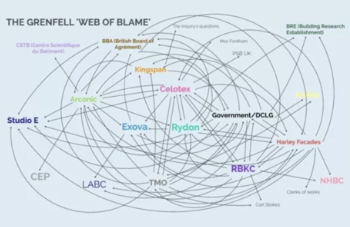
Government responds to the final Grenfell Inquiry report
A with a brief summary with reactions to their response.
A brief description and background to this new February law.
Everything you need to know about building conservation and the historic environment.
NFCC publishes Industry White Paper on Remediation
Calling for a coordinated approach and cross-departmental Construction Skills Strategy to manage workforce development.
'who blames whom and for what, and there are three reasons for doing that: legal , cultural and moral"
How the Home Energy Model will be different from SAP
Comparing different building energy models.
Mapping approaches for standardisation.
UK Construction contract spending up at the start of 2025
New construction orders increase by 69 percent on December.
Preparing for the future: how specifiers can lead the way
As the construction industry prepares for the updated home and building efficiency standards.
Embodied Carbon in the Built Environment
A practical guide for built environment professionals.
Updating the minimum energy efficiency standards
Background and key points to the current consultation.
Heritage building skills and live-site training.
Shortage of high-quality data threatening the AI boom
And other fundamental issues highlighted by the Open Data Institute.
Data centres top the list of growth opportunities
In robust, yet heterogenous world BACS market.
Increased funding for BSR announced
Within plans for next generation of new towns.