Polite architecture
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
Polite architecture is the term used to describe buildings that incorporate non-local styles and use designed features that go beyond functional requirements. These stylistic features may be used by the architect to make a particular statement or to achieve an aesthetically-pleasing effect.
As a concept of architectural theory it is often used as a contrast with vernacular architecture. The vernacular is a type of architecture which is indigenous to a specific time and place, and historically uses the skills and expertise of local builders as opposed to formally-trained architects. Polite architecture often incorporates national or international architectural fashions, styles and conventions and seldom pays any regard to materials or practices particular to a locality.
Although there are buildings that are either wholly vernacular or polite, the terms are often a matter of subjectivity and many buildings incorporate both.
[edit] Historical context
Historically, buildings characterised as ‘polite’ were the reserve of wealthy individuals and institutions who could afford buildings that included individual style as opposed to being purely functional. Since the developed world’s industrialisation, elements of ‘the polite’ began to proliferate, due largely to the expansion and professionalisation of the field of architecture. The growing availability of more aesthetically-pleasing materials such as decorative bricks, metals, plastics and glass, as well as the infrastructure to be able to source them from beyond the immediate locale also played a role in the rise of ‘the polite’ form during the late 18th and 19th centuries.
As architects became increasingly influential figures, polite designs have continued to be in demand throughout the 20th and 21st centuries, despite some modernist designers attempting to abandon style altogether. The desire for architectural revivalism of many different styles, such as gothic and classical, has also played an important part in the continuing health of ‘the polite’ form.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- Aesthetic movement.
- Architectural styles.
- Bauhaus.
- Context.
- Contextualism.
- Design methodology.
- English architectural stylistic periods.
- Nineteenth century architecture.
- The history of fabric structures.
- Vernacular architecture.
[edit] External references
Featured articles and news
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this...
National Apprenticeship Week 2026, 9-15 Feb
Shining a light on the positive impacts for businesses, their apprentices and the wider economy alike.
Applications and benefits of acoustic flooring
From commercial to retail.
From solid to sprung and ribbed to raised.
Strengthening industry collaboration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong Institute of Construction and The Chartered Institute of Building sign Memorandum of Understanding.
A detailed description fron the experts at Cornish Lime.
IHBC planning for growth with corporate plan development
Grow with the Institute by volunteering and CP25 consultation.
Connecting ambition and action for designers and specifiers.
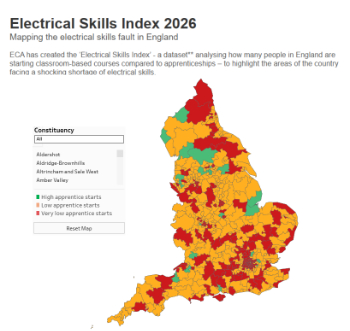
Electrical skills gap deepens as apprenticeship starts fall despite surging demand says ECA.
Built environment bodies deepen joint action on EDI
B.E.Inclusive initiative agree next phase of joint equity, diversity and inclusion (EDI) action plan.
Recognising culture as key to sustainable economic growth
Creative UK Provocation paper: Culture as Growth Infrastructure.
Futurebuild and UK Construction Week London Unite
Creating the UK’s Built Environment Super Event and over 25 other key partnerships.
Welsh and Scottish 2026 elections
Manifestos for the built environment for upcoming same May day elections.
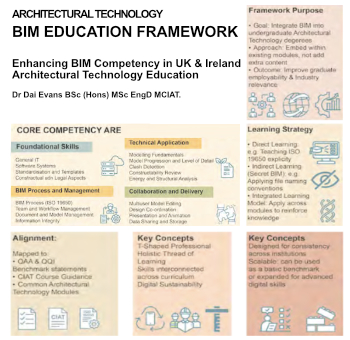
Advancing BIM education with a competency framework
“We don’t need people who can just draw in 3D. We need people who can think in data.”
Guidance notes to prepare for April ERA changes
From the Electrical Contractors' Association Employee Relations team.
Significant changes to be seen from the new ERA in 2026 and 2027, starting on 6 April 2026.
First aid in the modern workplace with St John Ambulance.
Solar panels, pitched roofs and risk of fire spread
60% increase in solar panel fires prompts tests and installation warnings.
Modernising heat networks with Heat interface unit
Why HIUs hold the key to efficiency upgrades.