Metaverse
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
The metaverse (sometimes referred to as extended reality) is a modern buzzword that has been associated with the Internet of the future. It has been described as a robust, responsive, inclusive, version of virtual experiences, environments and assets.
Nick Kelly, Senior Lecturer in Interaction Design, Queensland University of Technology, calls the metaverse “A high-tech plan to Facebookify the world”. He explains that in a June 2021 announcement, Facebook Chief Executive Mark Zuckerberg said the organisation would move away from its position as a social media company to becoming “a metaverse company”, functioning in an “embodied Internet” that blends real and virtual worlds more than ever before.
[edit] History
The term 'metaverse' was first introduced in 1992 by science fiction writer Neal Stephenson. The author recognised the need to name the existence of a futuristic world that combined physical and fabricated reality.
In justifying the greater adoption of the term metaverse, Kelly says existing terms ‘don’t capture the new social relationships, sensory experiences and economic behaviours that are emerging along with these extensions to the virtual….Neologisms such as “the Cloud” or the “Internet of Things” have stuck with us precisely because they are handy ways to refer to technologies that are becoming increasingly important. The metaverse sits in this same category.’
[edit] The possible impact of the metaverse
Kelly proposes ways in which new concepts such as the metaverse will shape society, politics and culture in a form of ‘“technological determinism”: the sense that advances in technology shape our social relations, power relations and culture in a way that helps to organise our societies more productively. Shared standards and protocols that bring disparate virtual worlds and augmented realities into a single, open metaverse could help people work together and cut down on duplication of effort.’
Kelly presents the example of a metaverse alliance that is being explored between private companies and the South Korean government. This alliance is attempting to work together to develop an open, national VR platform. Kelly writes, ‘A big part of this is finding ways to blend smartphones, 5G networks, augmented reality, virtual currencies and social networks to solve problems for society (and, more cynically, make profits).’
While arrangements such as the metaverse alliance may result in beneficial collaborations, there are also drawbacks associated with shifting a physical reality to one that is primarily based on virtual interactions. Kelly says that in a metaverse, varied realities are not compatible with ‘a “one-world world” - a reality that does not permit other realities.’
He suggests this may be limiting in terms of connections to people and the development of communities, despite the fact ‘it offers us limitless possibilities to overcome the constraints of the physical world; yet in doing so, only replaces them with constraints imposed by what the metaverse will allow.’
The article 'What is the metaverse? A high-tech plan to Facebookify the world' was written by Nick Kelly, Senior Lecturer in Interaction Design, Queensland University of Technology. It was published on 6 August 2021 on The Conversation website under a Creative Commons license.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
Featured articles and news
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this...
National Apprenticeship Week 2026, 9-15 Feb
Shining a light on the positive impacts for businesses, their apprentices and the wider economy alike.
Applications and benefits of acoustic flooring
From commercial to retail.
From solid to sprung and ribbed to raised.
Strengthening industry collaboration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong Institute of Construction and The Chartered Institute of Building sign Memorandum of Understanding.
A detailed description from the experts at Cornish Lime.
IHBC planning for growth with corporate plan development
Grow with the Institute by volunteering and CP25 consultation.
Connecting ambition and action for designers and specifiers.
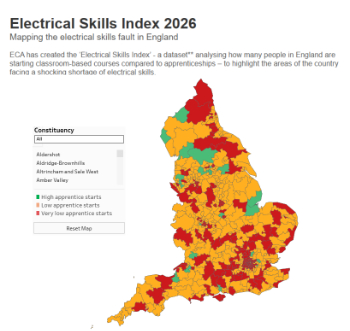
Electrical skills gap deepens as apprenticeship starts fall despite surging demand says ECA.
Built environment bodies deepen joint action on EDI
B.E.Inclusive initiative agree next phase of joint equity, diversity and inclusion (EDI) action plan.
Recognising culture as key to sustainable economic growth
Creative UK Provocation paper: Culture as Growth Infrastructure.
Futurebuild and UK Construction Week London Unite
Creating the UK’s Built Environment Super Event and over 25 other key partnerships.
Welsh and Scottish 2026 elections
Manifestos for the built environment for upcoming same May day elections.
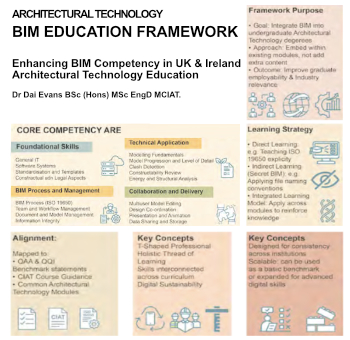
Advancing BIM education with a competency framework
“We don’t need people who can just draw in 3D. We need people who can think in data.”