Gentrification
The term ‘gentrification’ refers to changes that occur over time as a direct or indirect result of people on higher incomes purchasing or renting property in low income or ‘working class’ areas.
In an urban context, gentrification is associated with movement and can be viewed positively, in that it drives investment and economic prosperity to an area; and negatively, in that there is the perception that the traditional character and culture of an area becomes diluted and gradually rendered obsolete.
The term derives from the word ‘gentry’ which historically referred to people with wealth, although it originates from the Old French ‘genterise’ meaning ‘of gentle birth’ which became anglicised as ‘gentleman’. The term itself was coined by the sociologist Ruth Glass in 1964 in response to the influx of middle-class people to the cities which she saw as displacing ‘lower-class’ residents.
Urban theorists broadly agree in the belief that before an area becomes gentrified it must experience a period of disinvestment and decline. During this period, median income levels decline, infrastructure and buildings fall into disrepair, and businesses relocate elsewhere. These are often described as ‘urban wastelands’.
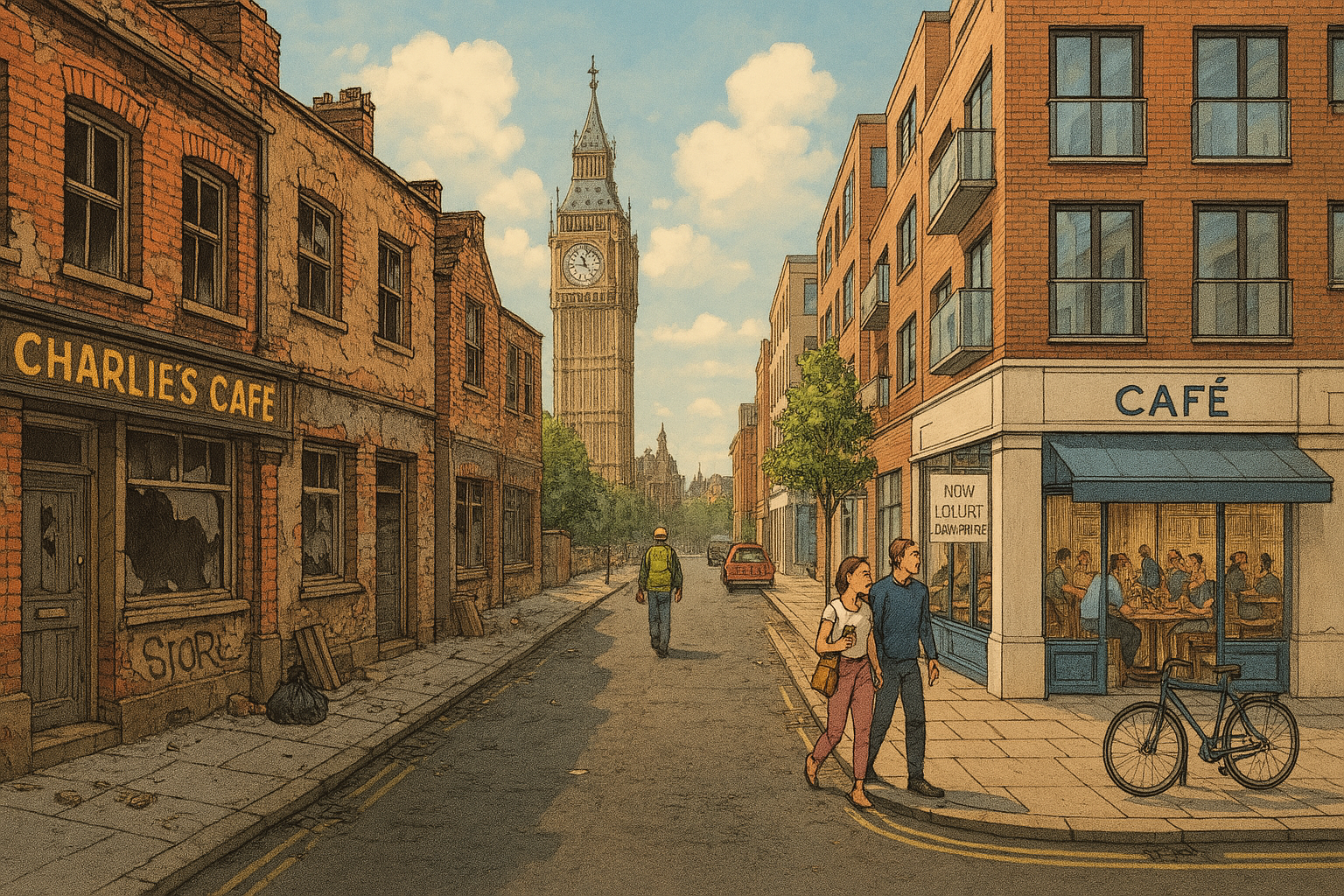
At some point in this period of decline, the area starts to attract people who are predominantly young, educated, artistically-minded, and with some level of disposable income. Artist communities, exhibition and performance spaces, underground music venues, and independent shops begin to appear in abandoned industrial spaces, as the area develops a reputation for being ‘alternative’, ‘edgy’ and ‘bohemian’, reflecting the lifestyles and tastes of those who move there.
Where once an area may have been viewed as unwelcoming or dangerous, it slowly becomes a more attractive prospect to real estate developers and wealthier young people who may be moving into a city from the suburbs or elsewhere. Responding to the interest, developers may seek to buy and regenerate old buildings, creating new apartments which gradually push property prices higher. As this happens, the reputation of the area as being ‘alternative’ and ‘interesting’ starts to diminish; independent businesses are replaced by chain stores, the unique character of the area becomes more homogenised.
The firmest indication of gentrification is an increase in property prices, rents and taxes in a particular district. This usually correlates with the increased incomes of people arriving in the area. As a result, those on lower incomes are ‘priced out’ of the area, and it slowly becomes economically homogeneous.
Political initiatives often have the effect of promoting gentrification, by introducing deferred taxes for real estate companies, mortgage incentives for first-time buyers, and financial incentives for the owners of rental housing or other buildings that require renovation.
One of the main advantages of gentrification is that old industrial buildings are renovated and redeveloped which can make the area more visually appealing and reduce crime rates. It can also reduce vacancy rates and encourage further development and business investment, which can increase employment opportunities.
The rise in property values cause taxes based on values to increase; but this can result in owners unable to pay the taxes being forced to sell their property and move to a cheaper community.
Rent controls are seen as one potential action that can combat gentrification pricing out local residents. However, controls can be counter-productive, and cities such as New York have found that they reduce the number of available rental properties, or subsidise wealthy inhabitants. Other measures are similarly controversial, such as demands that new builds provide socially-affordable housing provision, which leads to complaints that such accommodation is often of poor quality or sold by developers to overseas investors, leaving lucrative properties empty.
Examples of urban gentrification that some consider to have had a net-positive effect include the areas of Shoreditch and Hackney in East London; Brixton in South London; Brooklyn in New York; and Kreuzberg in Berlin.
See also: Gentrification in London
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
- Affordable housing.
- Central business district (CBD).
- Densification.
- Edge Debate 71 - Can decentralisation solve the housing crisis?
- Gentrification in London
- Housing associations.
- Must cities grow to compete?
- Private rented sector.
- Public space.
- Regeneration.
- Shared heritage from a social perspective.
- Social housing.
- Suburb.
- The compact sustainable city.
- The future of the green belt.
- Town planning.
- Urban decay.
- Urban design.
- Urban sprawl.
Featured articles and news
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.
The 2025 draft NPPF in brief with indicative responses
Local verses National and suitable verses sustainable: Consultation open for just over one week.
Increased vigilance on VAT Domestic Reverse Charge
HMRC bearing down with increasing force on construction consultant says.
Call for greater recognition of professional standards
Chartered bodies representing more than 1.5 million individuals have written to the UK Government.