Catacomb
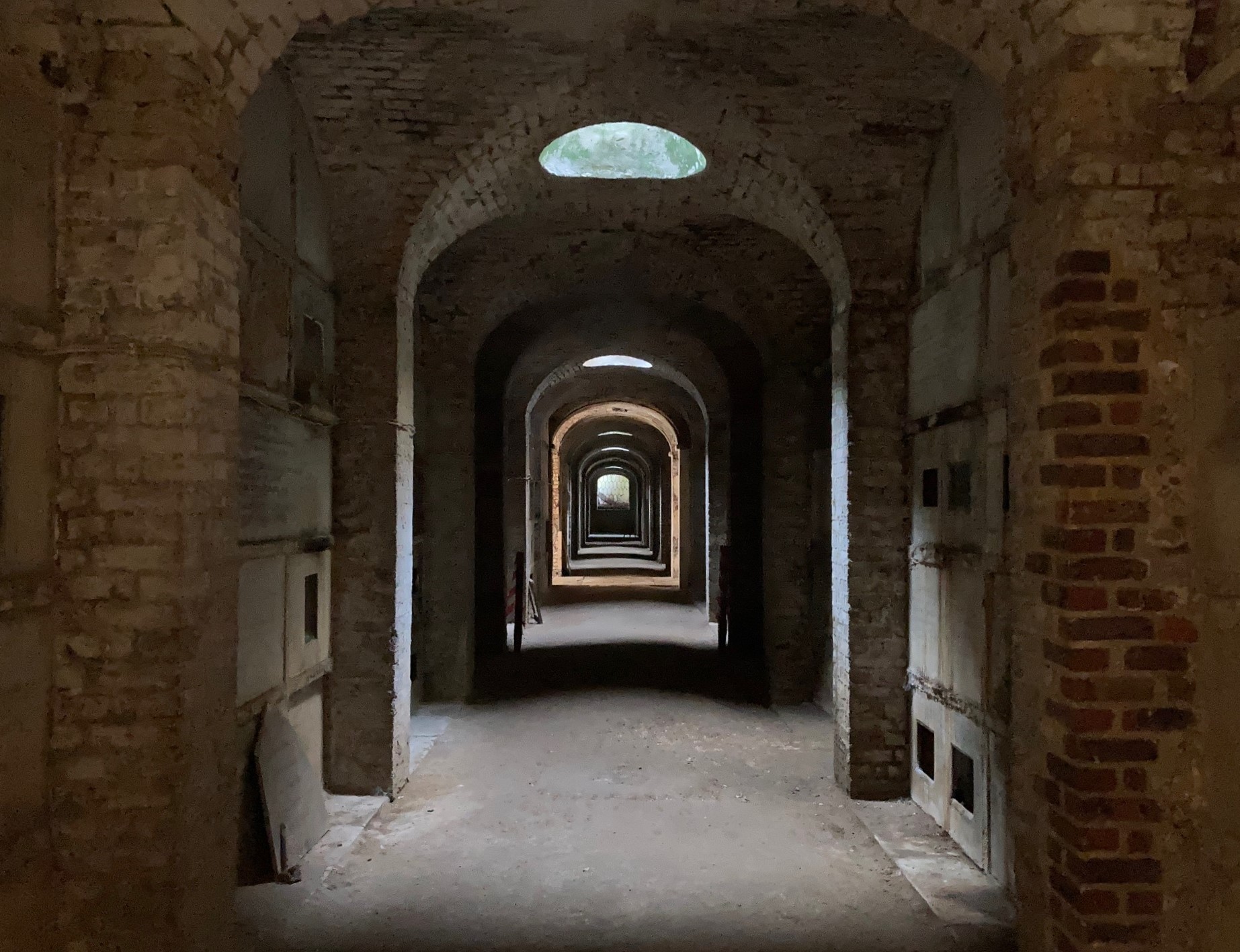 Inside the Terrace catacombs at Highgate cemetery, there is a brick-vaulted gallery that is naturally illuminated by oculi set in the terrace above. The spaces were used as both temporary and permanent resting places. Inside the Terrace catacombs at Highgate cemetery, there is a brick-vaulted gallery that is naturally illuminated by oculi set in the terrace above. The spaces were used as both temporary and permanent resting places.
|
The Penguin Dictionary of Architecture (third edition) was published in 1980. It was created for Penguin Reference and compiled by John Fleming, Hugh Honour and Nikolaus Pevsner. It defines a catacomb as: ‘An underground cemetery, sometimes on several levels, consisting of linked galleries and chambers with recesses for tombs (loculi).’
It is believed that the term catacomb was first used to describe a third century Christian underground burial chamber located outside Rome. During this period, it was illegal to bury the dead within the walls of the city.
This manner of burial was used in other parts of Italy, where a tradition of fresco painting on catacomb walls emerged as an early form of Christian art. Carvings also decorate the walls in some instances.
Catacombs fell out of fashion before the sixth century, but they became more popular again in the 1700s, when subterranean building was common in many parts of the world.
Some noteworthy examples include:
- San Gennaro catacombs in Naples.
- Paris catacombs (which hold the bones of more than six million people and was used by the French Resistance during the Second World war).
- Odessa catacombs (which were used for mining not for burial purposes).
London has its own catacombs, including those of Highgate Cemetery. These brick vaulted structures - referred to as the Terrace catacombs - are believed to be one of the earliest examples of asphalted construction in England.
|
These are some of the coffins stored in the recesses of Highgate cemetery's catacombs. |
Dating from the 1830s, this structure has separate recesses for 825 coffins, including one for the British surgeon, Robert Liston. Liston specialised in amputations and introduced the use of anaesthesia - outside the United States - for operations.
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
ECA support for Gate Safe’s Safe School Gates Campaign.
Core construction skills explained
Preparing for a career in construction.
Retrofitting for resilience with the Leicester Resilience Hub
Community-serving facilities, enhanced as support and essential services for climate-related disruptions.
Some of the articles relating to water, here to browse. Any missing?
Recognisable Gothic characters, designed to dramatically spout water away from buildings.
A case study and a warning to would-be developers
Creating four dwellings... after half a century of doing this job, why, oh why, is it so difficult?
Reform of the fire engineering profession
Fire Engineers Advisory Panel: Authoritative Statement, reactions and next steps.
Restoration and renewal of the Palace of Westminster
A complex project of cultural significance from full decant to EMI, opportunities and a potential a way forward.
Apprenticeships and the responsibility we share
Perspectives from the CIOB President as National Apprentice Week comes to a close.
The first line of defence against rain, wind and snow.
Building Safety recap January, 2026
What we missed at the end of last year, and at the start of this...
National Apprenticeship Week 2026, 9-15 Feb
Shining a light on the positive impacts for businesses, their apprentices and the wider economy alike.
Applications and benefits of acoustic flooring
From commercial to retail.
From solid to sprung and ribbed to raised.
Strengthening industry collaboration in Hong Kong
Hong Kong Institute of Construction and The Chartered Institute of Building sign Memorandum of Understanding.
A detailed description from the experts at Cornish Lime.
IHBC planning for growth with corporate plan development
Grow with the Institute by volunteering and CP25 consultation.
Connecting ambition and action for designers and specifiers.
Electrical skills gap deepens as apprenticeship starts fall despite surging demand says ECA.
Built environment bodies deepen joint action on EDI
B.E.Inclusive initiative agree next phase of joint equity, diversity and inclusion (EDI) action plan.
Recognising culture as key to sustainable economic growth
Creative UK Provocation paper: Culture as Growth Infrastructure.