Ashlar
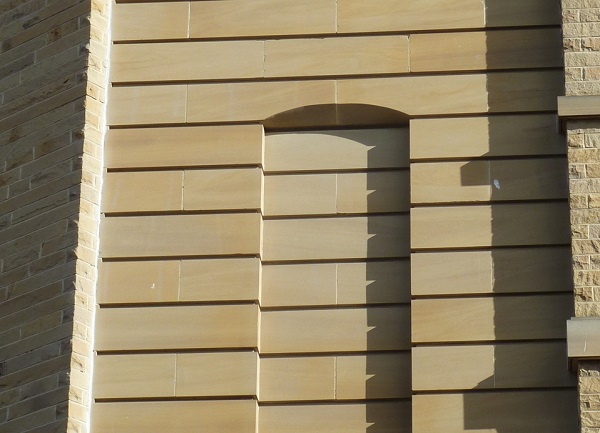
Ashlar is a type of masonry which is finely cut and/or worked, and is characterised by its smooth, even faces and square edges. It can also be used to refer to an individual stone that has been finely cut and worked until squared.
Ashlar has been used in construction as an alternative to brick or other materials dating back to classical architecture, where it was often used to contrast with rustication (masonry with a purposefully rough or patterned surface).
Courses of ashlar can be horizontal, with blocks laid in parallel, or may be random with deliberately discontinuous vertical and horizontal joints.
Since ashlar blocks are precisely cut on all faces which are adjacent to other masonry, very thin joints can be achieved. The face of the block away from joints may be left rough and unpolished (known as quarry-faced), or may be polished or rendered decoratively. Mason’s drag is a form of decoration used on softer stone ashlar which involves small grooves applied by a metal comb-like device.
Mortar, or another joining material, is used to bind ashlar blocks together. Other methods of assembly such as metal ties can be used, in a process known as dry ashlar. Such a technique can be seen in the Inca architecture of Cusco and Machu Picchu.
In the UK, ashlar walling can be found in many historic buildings; one notable example being the Royal Crescent in Bath. It is also becoming more popular as a form of exterior cladding in urban commercial developments.
Society for the Protection of Ancient Buildings (SPAB) definition from their online Glossary : 'Finely dressed stone laid in regular courses with thin joints.'
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings
Featured articles and news
Delivering radical reform in the UK energy market
What are the benefits, barriers and underlying principles.
Information Management Initiative IMI
Building sector-transforming capabilities in emerging technologies.
Recent study of UK households reveals chilling home truths
Poor insulation, EPC knowledge and lack of understanding as to what retrofit might offer.
Embodied Carbon in the Built Environment
Overview, regulations, detail calculations and much more.
Why the construction sector must embrace workplace mental health support
Let’s talk; more importantly now, than ever.
Refurbishment for net zero; the BSRIA white paper
The everyday practice of tackling energy efficiency, fabric first, ventilation, air quality, and occupant wellbeing.
Sustainable construction design teams survey
Shaping the Future of Sustainable Design: Your Voice Matters.
Ensuring the trustworthiness of AI systems
A key growth area, including impacts for construction.
Foundations for the Future: A new model for social housing
To create a social housing pipeline, that reduces the need for continuous government funding.
Mutual Investment Models or MIMs
PPP or PFI, enhanced for public interest by the Welsh Government.
Stress Awareness Week ends but employer legal duties continue.
A call to follow the five Rs for the business and for the staff.
Key points and relevance to construction of meeting, due to reconvene.
Cladding remediation programmes, transparency and target date.
National Audit Office issue report on cladding remediation.
HBPT and BEAMS Jubilees. Book review.
Does the first Labour budget deliver for the built environment?
What does the UK Budget mean for electrical contractors?
Mixed response as business pays, are there silver linings?